Interacting with the Conviction Voting Precompile¶
Introduction¶
As a Polkadot parachain and decentralized network, Moonbeam features native on-chain governance that enables stakeholders to participate in the direction of the network. With the introduction of OpenGov, also referred to as Governance v2, the Conviction Voting Pallet allows token holders to make, delegate, and manage Conviction-weighted votes on referenda. To learn more about Moonbeam's governance system, such as an overview of related terminology, principles, mechanics, and more, please refer to the Governance on Moonbeam page.
The Conviction Voting Precompile interacts directly with Substrate's Conviction Voting Pallet. This pallet is coded in Rust and is normally not accessible from the Ethereum API side of Moonbeam. However, the Conviction Voting Precompile allows you to access governance-related functions of the Substrate Conviction Voting Pallet directly from a Solidity interface. Additionally, this enables a vastly improved end-user experience. For example, token holders can vote on referenda or delegate a vote directly from MetaMask, rather than importing an account in Polkadot.js Apps and navigating a complex UI.
The Conviction Voting Precompile is located at the following address:
0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000812
0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000812
0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000812
Note
There can be some unintended consequences when using the precompiled contracts on Moonbeam. Please refer to the Security Considerations page for more information.
The Conviction Voting Solidity Interface¶
ConvictionVoting.sol is a Solidity interface that allows developers to interact with the precompile's methods.
The interfaces includes a Conviction enum that defines the Conviction multiplier types. The enum has the following variables:
- None - 0.1x votes, unlocked
- Locked1x - 1x votes, locked for an Enactment Period following a successful vote
- Locked2x - 2x votes, locked for 2x Enactment Period following a successful vote
- Locked3x - 4x votes, locked for 4x Enactments Period following a successful vote
- Locked4x - 8x votes, locked for 8x Enactments Period following a successful vote
- Locked5x - 16x votes, locked for 16x Enactments Period following a successful vote
- Locked6x - 32x votes, locked for 32x Enactments Period following a successful vote
The interface includes the following functions:
votingFor(address who, uint16 trackId) - returns the votes for a given account and Track
who- address of the account to query the votes fortrackId- uint16 Track ID where the requested changes need to occur
classLocksFor(address who) - returns the class locks for a given account
who- address of the account to query the class locks for
voteYes(uint32 pollIndex, uint256 voteAmount, Conviction conviction) - votes a Conviction-weighted "Aye" on a poll (referendum)
pollIndex- uint32 index of the poll (referendum)voteAmount- uint256 balance to be locked for the voteconviction- Conviction represents a value from the aforementionedConvictionenum
voteNo(uint32 pollIndex, uint256 voteAmount, Conviction conviction) - votes a Conviction-weighted "Nay" on a poll (referendum)
pollIndex- uint32 index of the poll (referendum)voteAmount- uint256 balance to be locked for the voteconviction- Conviction represents a value from the aforementionedConvictionenum
voteSplit(uint32 pollIndex, uint256 aye, uint256 nay) - votes a split vote, with a given amount locked for "Aye" and a given amount locked for "Nay", on a poll (referendum)
pollIndex- uint32 index of the poll (referendum)aye- uint256 balance to be locked for the "Aye" votenay- uint256 balance to be locked for the "Nay" vote
voteSplitAbstain(uint32 pollIndex, uint256 aye, uint256 nay) - votes a split abstained vote, with a given amount locked for "Aye", a given amount locked for "Nay", and a given amount locked for an abstain vote (support), on a poll (referendum)
pollIndex- uint32 index of the poll (referendum)aye- uint256 balance to be locked for the "Aye" votenay- uint256 balance to be locked for the "Nay" vote
removeVote(uint32 pollIndex) - removes a vote in a poll (referendum).
pollIndex- uint32 index of the poll (referendum)
removeVoteForTrack(uint32 pollIndex, uint16 trackId) - removes a vote from a specific track in a poll (referendum).
pollIndex- uint32 index of the poll (referendum)trackId- uint16 Track ID where the requested changes need to occur
removeOtherVote(address target, uint16 trackId, uint32 pollIndex) - removes a vote in a poll (referendum) for another voter.
target- address that has a vote or tokens to be removed or unlockedtrackId- uint16 Track ID where the requested changes need to occurpollIndex- uint32 index of the poll (referendum)
delegate(uint16 trackId, address representative, Conviction conviction, uint256 amount) - delegates another account as a representative to place a Conviction-weighted vote on the behalf of the sending account for a specific Track
trackId- uint16 Track ID where the requested changes need to occurrepresentative- address of the account to be delegated as representativeconviction- Conviction represents a value from the aforementionedConvictionenumamount- uint256 balance to be delegated
undelegate(uint16 trackId) - removes the caller's vote delegations for a specific Track
trackId- uint16 Track ID where the requested changes need to occur
unlock(uint16 trackId, address target) - unlocks the locked tokens of a specific account for a specific Track
trackId- uint16 Track ID where the requested changes need to occurtarget- address that has a vote or tokens to be removed or unlocked
The interface also includes the following events:
- Voted(uint32 indexed pollIndex, address voter, bool aye, uint256 voteAmount, uint8 conviction) - emitted when an account makes a vote
- VoteSplit(uint32 indexed pollIndex, address voter, uin256 aye, uint256 nay) - emitted when an account makes a split vote
- VoteSplitAbstained(uint32 indexed pollIndex, address voter, uin256 aye, uint256 nay, uint256 nay) - emitted when an account makes a split abstained vote
- VoteRemoved(uint32 indexed pollIndex, address voter) - emitted when an account's (
voter) vote has been removed from an ongoing poll (referendum) - VoteRemovedForTrack(uint32 indexed pollIndex, uint16 trackId, address voter) - emitted when an account's (
voter) vote has been removed from an ongoing poll (referendum) for a specific Track - VoteRemovedOther(uint32 indexed pollIndex, address caller, address target, uint16 trackId) - emitted when an account (
caller) removed a vote for another account (target) - Delegated(uint16 indexed trackId, address from, address to, uint256 delegatedAmount, uint8 conviction) - emitted when an account (
from) delegates a Conviction-weighted vote of a given amount to another account (to) - Undelegated(uint16 indexed trackId, address caller) - emitted when an account's (
caller) delegations are removed for a specific Track - Unlocked(uint16 indexed trackId, address caller) - emitted when an account's (
caller) locked tokens are unlocked for a specific Track
Interact with the Solidity Interface¶
Checking Prerequisites¶
The below example is demonstrated on Moonbase Alpha, however, similar steps can be taken for Moonriver. To follow the steps in this guide, you'll need to have the following:
- MetaMask installed and connected to Moonbase Alpha
- An account with some DEV tokens. You can get DEV tokens for testing on Moonbase Alpha once every 24 hours from the Moonbase Alpha Faucet
Remix Set Up¶
- Click on the File explorer tab
- Paste a copy of
ConvictionVoting.solinto a Remix file namedConvictionVoting.sol
Compile the Contract¶
- Click on the Compile tab, second from top
- Then to compile the interface, click on Compile ConvictionVoting.sol
Access the Contract¶
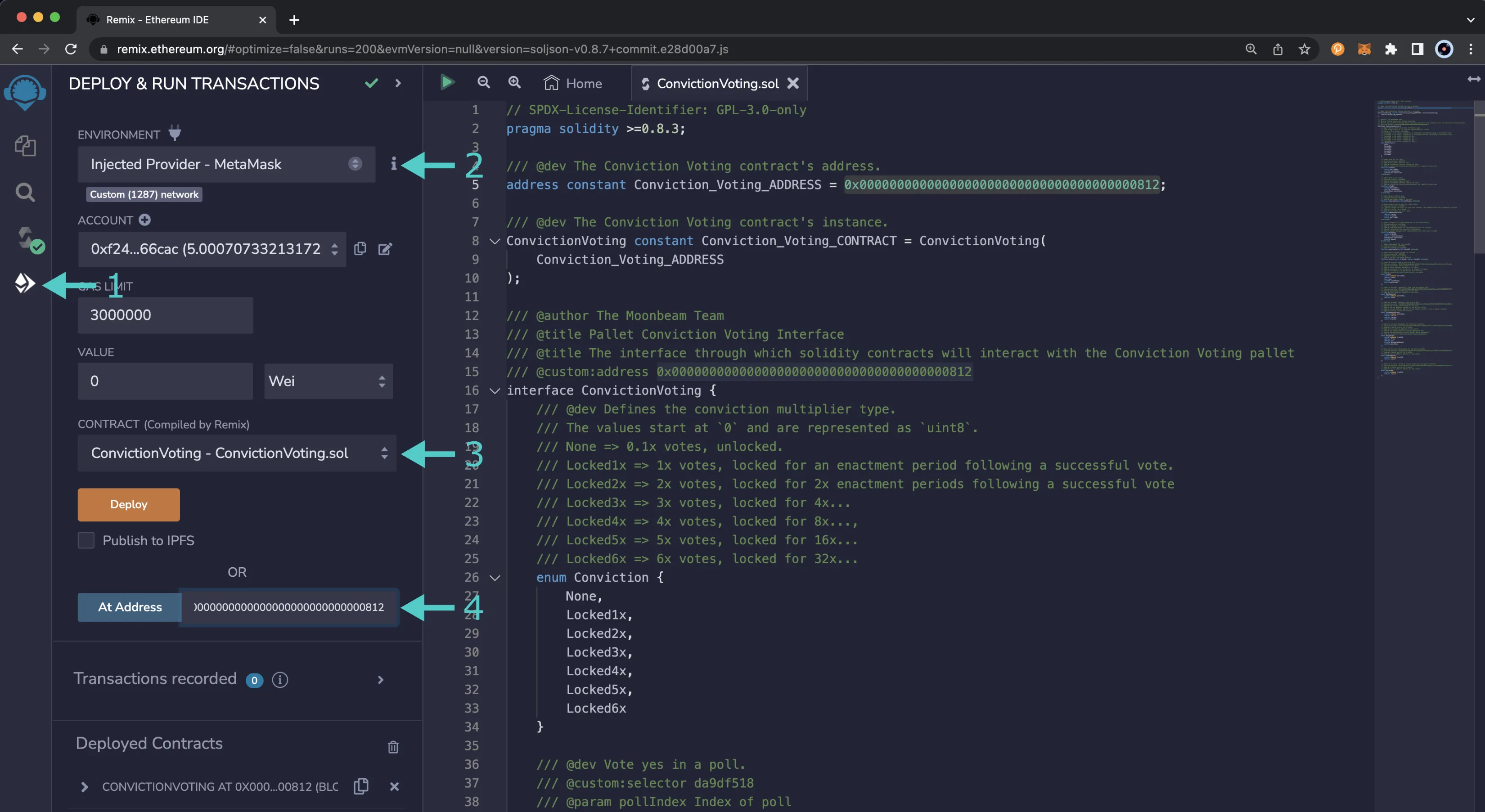
- Click on the Deploy and Run tab, directly below the Compile tab in Remix. Note: you are not deploying a contract here, instead you are accessing a precompiled contract that is already deployed
- Make sure Injected Provider - Metamask is selected in the ENVIRONMENT drop down
- Ensure ConvictionVoting.sol is selected in the CONTRACT dropdown. Since this is a precompiled contract there is no need to deploy, instead you are going to provide the address of the precompile in the At Address field
- Provide the address of the Conviction Voting Precompile for Moonbase Alpha:
0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000812and click At Address - The Conviction Voting Precompile will appear in the list of Deployed Contracts
Vote on a Referendum¶
You can lock tokens and vote on a referendum at anytime during the Lead-in Period or the Decide Period. In order for a referendum to pass, it needs to garner minimum Approval and Support, which vary by track. For more information on each of the relative periods and the Approval and Support requirements by Track, please refer to the OpenGov section of the governance overview page.
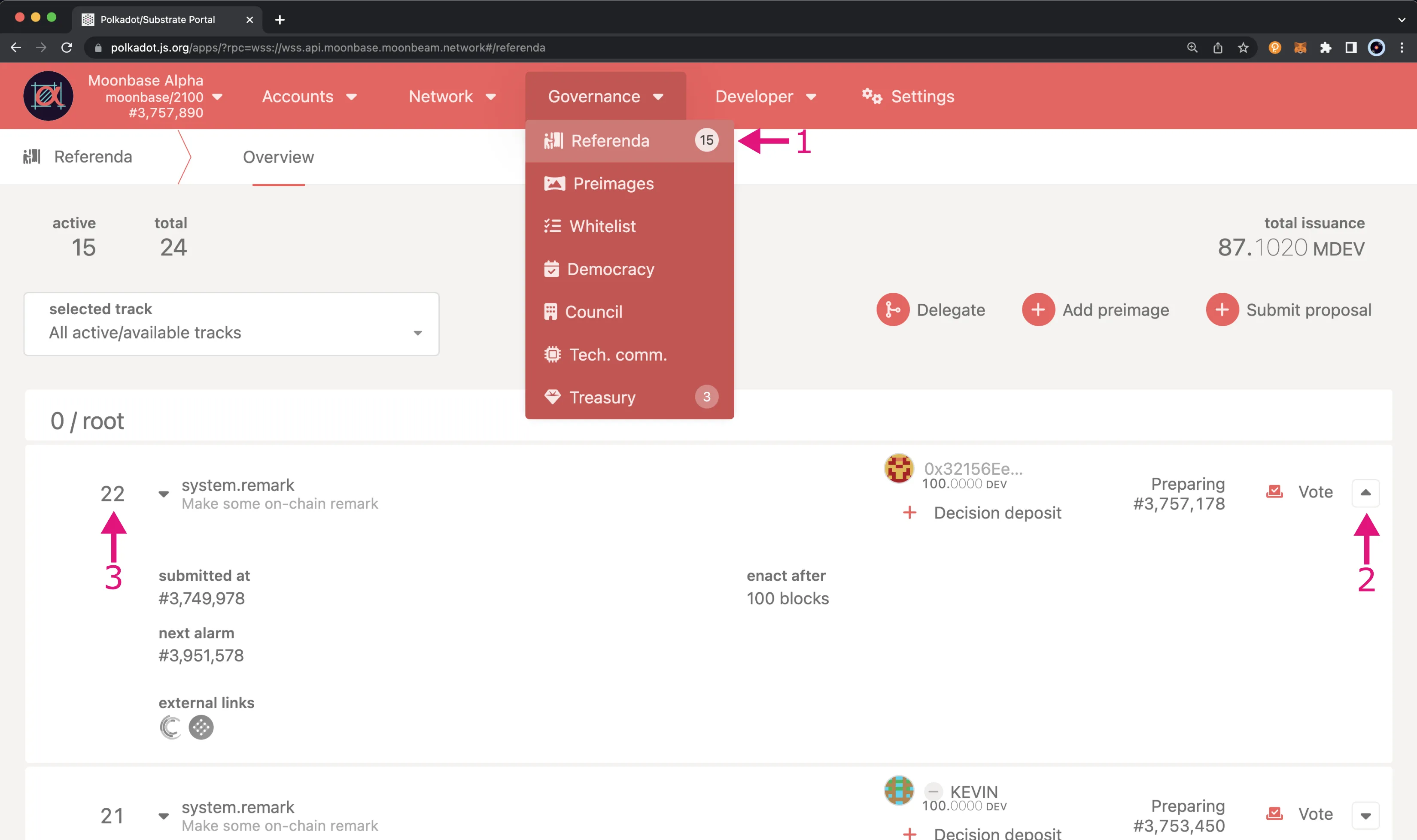
First, you'll need to get the index of the referendum you wish to vote on. To get the index of a referendum, head to Polkadot.js Apps and take the following steps:
- From the Governance tab dropdown, select Referenda
- Look for the referenda you want to vote on. You can view more details about a specific referendum by clicking on the triangle icon. If there is no triangle icon, this means that only a proposal hash, and no preimage has been submitted for the proposal
- Take note of the referendum index
Now, you're ready to return to Remix to vote on the referendum via the Conviction Voting Precompile. There are two methods you can use to vote on a referendum: voteYes or voteNo. As you probably have already figured out, if you're in agreement with the proposal, you'll use voteYes and if in disagreement, you'll use voteNo. You'll specify the amount of tokens you want to lock with your vote and the Conviction, using index of the Conviction you want to vote with in the aforementioned Conviction enum. For example, if you wanted to lock your tokens for the duration of two Enactment Periods following a successful vote, you would enter 2 for the Locked2x Conviction. For more information on Convictions, you can check out the Conviction Multiplier section of the Governance v2 documentation.
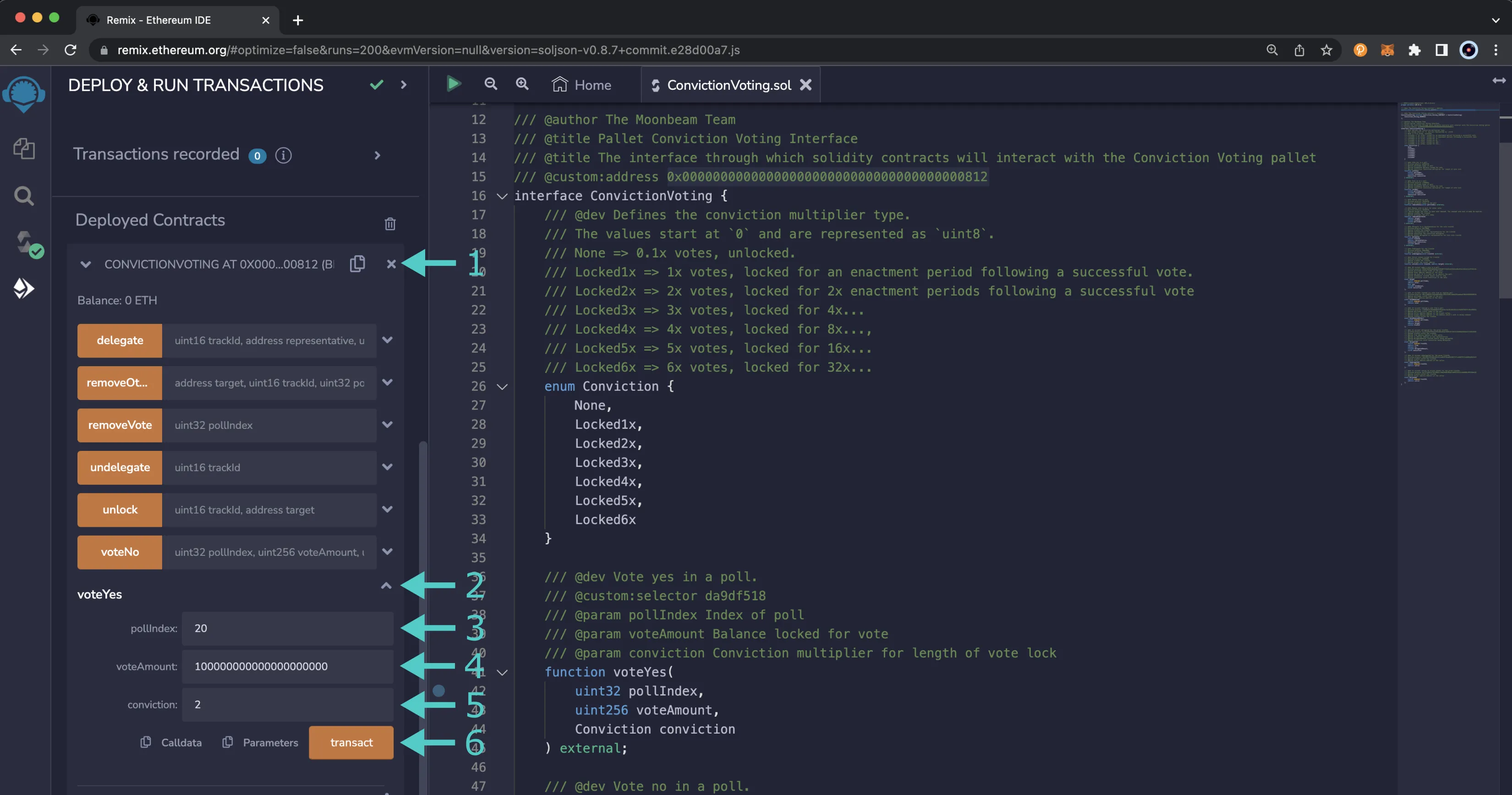
To submit your vote, you can take the following steps:
- Expand the Conviction Voting Precompile contract to see the available functions if it is not already open
- Find the voteYes or voteNo function, however you want to vote, and press the button to expand the section
- Enter the index of the referendum to vote on
- Enter the number of tokens to lock in Wei. Avoid entering your full balance here because you need to pay for transaction fees
- Enter the Conviction you want to vote with
- Press transact and confirm the transaction in MetaMask
Once the referendum has closed, you can use the Conviction Voting precompile to remove your vote and unlock your tokens.
Delegate a Vote¶
In addition to voting on a referendum yourself, you can delegate a Conviction-weighted vote to someone who is more knowledgeable on a particular topic to vote on your behalf, a process known as Vote Delegation. You can even delegate a different account for each of the Tracks.
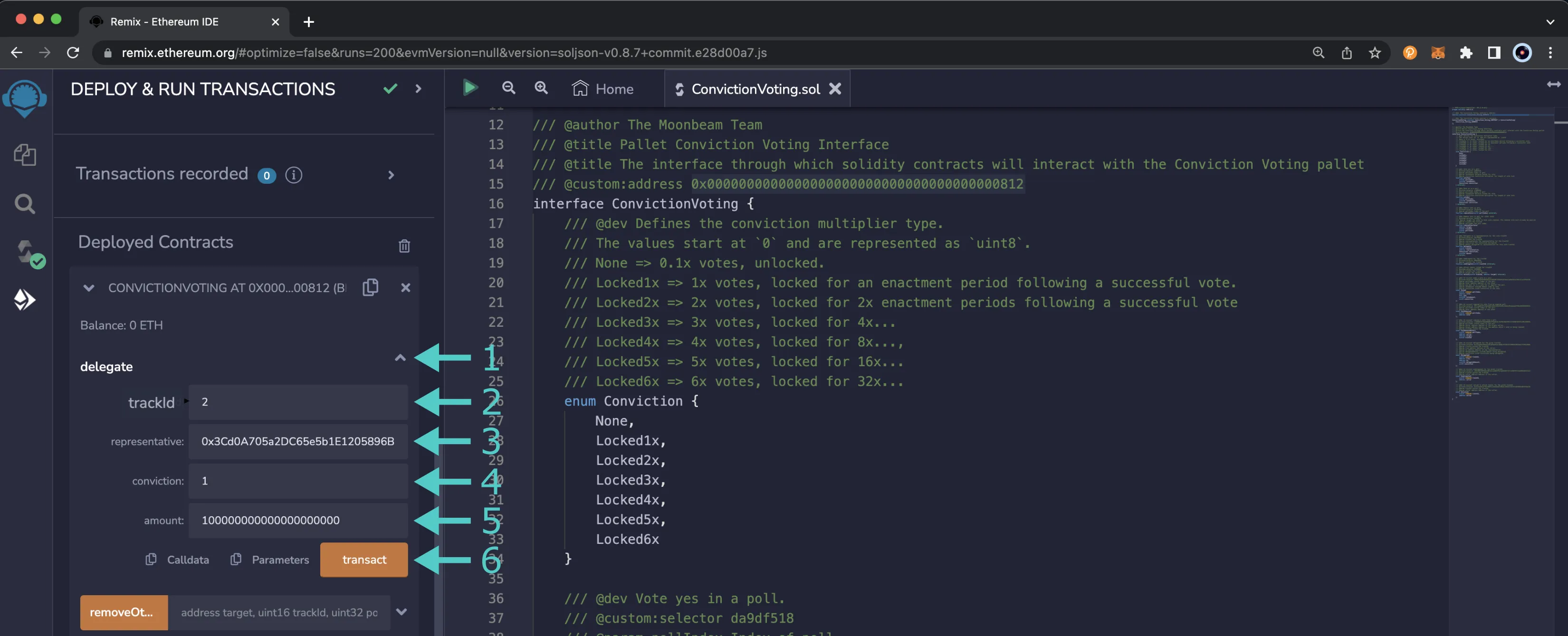
To get started, you can take the following steps:
- Find the delegate function and press the button to expand the section
- Enter the Track ID of the Track that you want the delegation to be used on. Track IDs can be found in the Referenda page of Polkadot.js Apps
- Enter the delegate account that will have the power to vote on your behalf
- Enter the number of tokens they can vote with in Wei. Avoid entering your full balance here because you need to pay for transaction fees
- Enter the Conviction they can vote with
- Press transact and confirm the transaction in MetaMask
Now the delegate account can vote on your behalf! If you no longer want a delegate vote to exist, you can remove it using the undelegate function of the Conviction Voting Precompile.
And that's it! You've completed your introduction to the Conviction Voting Precompile. There are a few more functions that are documented in ConvictionVoting.sol — feel free to reach out on Discord if you have any questions about those functions or any other aspect of the Conviction Voting Precompile.
| Created: February 15, 2023