Interacting with the Randomness Precompile¶
Introduction¶
Moonbeam utilizes verifiable random functions (VRF) to generate randomness that can be verified on-chain. A VRF is a cryptographic function that takes some input and produces random values, along with a proof of authenticity that these random values were generated by the submitter. The proof can be verified by anyone to ensure the random values generated were calculated correctly.
There are two available sources of randomness that provide random inputs based on block producers' VRF keys and past randomness results: local VRF and BABE epoch randomness. Local VRF is determined directly within Moonbeam using the collator of the block's VRF key and the last block's VRF output. On the other hand, BABE epoch randomness is based on all the VRF produced by the relay chain validators during a complete epoch.
For more information on the two sources of randomness, how the request and fulfillment process works, and security considerations, please refer to the Randomness on Moonbeam page.
Moonbeam provides a randomness precompile, which is a Solidity interface that enables smart contract developers to generate randomness via local VRF or BABE epoch randomness using the Ethereum API. Moonbeam also provides a randomness consumer Solidity contract that your contract must inherit from in order to consume fulfilled randomness requests.
This guide will show you how to use the randomness precompile and randomness consumer contract to create a lottery where the winners will randomly be selected. You'll also learn how to interact with the randomness precompile directly to perform actions such as purging an expired randomness request.
The randomness precompile is located at the following address:
0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000809
0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000809
0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000809
Note
There can be some unintended consequences when using the precompiled contracts on Moonbeam. Please refer to the Security Considerations page for more information.
The Randomness Solidity Interface¶
Randomness.sol is a Solidity interface that allows developers to interact with the precompile's methods.
Randomness.sol
// SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-3.0-only
pragma solidity >=0.8.3;
/// @dev The Randomness contract's address.
address constant RANDOMNESS_ADDRESS = 0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000809;
/// @dev The Randomness contract's instance.
Randomness constant RANDOMNESS_CONTRACT = Randomness(RANDOMNESS_ADDRESS);
/// @dev Maximum number of random words being requested
uint32 constant MAX_RANDOM_WORDS = 100;
/// @dev Minimum number of blocks before a request can be fulfilled for Local VRF Request
uint32 constant MIN_VRF_BLOCKS_DELAY = 2;
/// @dev Maximum number of blocks before a request can be fulfilled for Local VRF Request
uint32 constant MAX_VRF_BLOCKS_DELAY = 2000;
/// @dev The deposit amount needed to request random words. There is 1 deposit per request
uint256 constant REQUEST_DEPOSIT_AMOUNT = 1000000000000000000;
/// @author The Moonbeam Team
/// @title Pallet Randomness Interface
/// @dev The interface through which solidity contracts will interact with Randomness
/// @custom:address 0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000809
interface Randomness {
/// @notice Event emitted when the request has been successfully executed
event FulFillmentSucceeded();
/// @notice Event emitted when the request has failed to execute fulfillment
event FulFillmentFailed();
/// @notice The status of the request
/// @param DoesNotExist The request doesn't exist
/// @param Pending The request cannot be fulfilled yet
/// @param Ready The request is ready to be fulfilled
/// @param Expired The request has expired
enum RequestStatus {
DoesNotExist,
Pending,
Ready,
Expired
}
/// @notice The type of randomness source
/// @param LocalVRF Randomness VRF using the parachain material as seed
/// @param RelayBabeEpoch Randomness VRF using relay material from previous epoch
enum RandomnessSource {
LocalVRF,
RelayBabeEpoch
}
/// @notice The request details
/// @param id The id of the request (is always < 2**64)
/// @param refundAddress The address receiving the left-over fees after the fulfillment
/// @param contractAddress The address of the contract being called back during fulfillment
/// @param fee The amount to set aside to pay for the fulfillment
/// @param gasLimit The gas limit to use for the fulfillment
/// @param salt A string being mixed with the randomness seed to obtain different random words. This should be as unique as possible; using the same salt will lead to same randomness result.
/// @param numWords The number of random words requested (from 1 to MAX_RANDOM_WORDS)
/// @param randomnessSource The type of randomness source used to generate the random words
/// @param fulfillmentBlock The parachain block number at which the request can be fulfilled (for LocalVRF only)
/// @param fulfillmentEpochIndex The relay epoch index at which the request can be fulfilled (for RelayBabeEpoch)
/// @param expirationBlock The parachain block number at which the request expires (for LocalVRF only)
/// @param expirationEpochIndex The relay epoch index at which the request expires (for RelayBabeEpoch)
/// @param status The current status of the request
struct Request {
uint256 id;
address refundAddress;
address contractAddress;
uint256 fee;
uint256 gasLimit;
bytes32 salt;
uint32 numWords;
RandomnessSource randomnessSource;
uint32 fulfillmentBlock;
uint64 fulfillmentEpochIndex;
uint32 expirationBlock;
uint64 expirationEpochIndex;
RequestStatus status;
}
/// Return the current relay epoch index
/// @dev An epoch represents real time and not a block number
/// @dev Currently, time between epoch changes cannot be longer than:
/// @dev - Kusama/Westend/Rococo: 600 relay blocks (1 hour)
/// @dev - Polkadot: 2400 relay blocks (4 hours)
/// @custom:selector 81797566
function relayEpochIndex() external view returns (uint64);
/// Return the deposit required to perform a request
/// @dev Each request will need a deposit.
/// @custom:selector fb7cfdd7
function requiredDeposit() external view returns (uint256);
/// @notice Returns the request status
/// @param requestId The id of the request to check (must be < 2**64)
/// @return status Status of the request
/// @custom:selector d8a4676f
function getRequestStatus(uint256 requestId)
external
view
returns (RequestStatus status);
/// @notice Returns the request or revert
/// @param requestId The id of the request to check (must be < 2**64)
/// @return request The request
/// @custom:selector c58343ef
function getRequest(uint256 requestId)
external
view
returns (Request memory request);
/// @notice Request random words generated from the parachain VRF
/// @dev This is using pseudo-random VRF executed by the collator at the fulfillment
/// @dev Warning:
/// @dev The collator in charge of producing the block at fulfillment can decide to skip
/// @dev producing the block in order to have a different random word generated by the next
/// @dev collator, at the cost of a block reward. It is therefore economically viable to use
/// @dev this randomness source only if the financial reward at stake is lower than the block
/// @dev reward.
/// @dev In order to reduce the risk of a collator being able to predict the random words
/// @dev when the request is performed, it is possible to increase the delay to multiple blocks
/// @dev The higher the delay is, the less likely the collator will be able to know which
/// @dev collator will be in charge of fulfilling the request.
/// @dev Fulfillment is manual and can be executed by anyone (for free) after the given delay
/// @param refundAddress The address receiving the left-over fees after the fulfillment
/// @param fee The amount to set aside to pay for the fulfillment
/// @param gasLimit The gas limit to use for the fulfillment
/// @param salt A string being mixed with the randomness seed to obtain different random words
/// @param numWords The number of random words requested (from 1 to MAX_RANDOM_WORDS)
/// @param delay The number of blocks until the request can be fulfilled (between MIN_DELAY_BLOCKS and MAX_DELAY_BLOCKS)
/// @return requestId The id of the request requestLocalVRFRandomWords
/// @custom:selector 9478430c
function requestLocalVRFRandomWords(
address refundAddress,
uint256 fee,
uint64 gasLimit,
bytes32 salt,
uint8 numWords,
uint64 delay
) external returns (uint256);
/// @notice Request random words generated from the relaychain Babe consensus
/// @dev The random words are generated from the hash of the all the VRF provided by the
/// @dev relaychain validator during 1 epoch.
/// @dev It requires a delay of at least 1 epoch after the current epoch to be unpredictable
/// @dev at the time the request is performed.
/// @dev Warning:
/// @dev The validator (on the relaychain) of the last block of an epoch can decide to skip
/// @dev producing the block in order to choose the previous generated epoch random number
/// @dev at the cost of a relaychain block rewards. It is therefore economically viable to use
/// @dev this randomness source only if the financial reward at stake is lower than the relaychain
/// @dev block reward.
/// @dev (see https://crates.parity.io/pallet_babe/struct.RandomnessFromOneEpochAgo.html)
/// @dev Fulfillment is manual and can be executed by anyone (for free) at
/// @dev the beginning of the 2nd relay epoch following the current one
/// @param refundAddress The address receiving the left-over fees after the fulfillment
/// @param fee Amount to set aside to pay for the fulfillment. Those fees are taken from the contract
/// @param gasLimit Gas limit for the fulfillment
/// @param salt Salt to be mixed with raw randomness to get output
/// @param numWords Number of random words to be returned (limited to MAX_RANDOM_WORDS)
/// @return requestId The id of the request
/// @custom:selector 33c14a63
function requestRelayBabeEpochRandomWords(
address refundAddress,
uint256 fee,
uint64 gasLimit,
bytes32 salt,
uint8 numWords
) external returns (uint256);
/// @dev fulFill the request which will call the contract method "fulfillRandomWords"
/// @dev Fees of the caller are refunded if the request is fulfillable
/// @param requestId Request to be fulfilled (must be < 2**64)
/// @custom:selector 9a91eb0d
function fulfillRequest(uint256 requestId) external;
/// @param requestId Request receiving the additional fees (must be < 2**64)
/// @param feeIncrease Amount to increase
/// @custom:selector d0408a7f
function increaseRequestFee(uint256 requestId, uint256 feeIncrease)
external;
/// @param requestId Request to be purged (must be < 2**64)
/// @custom:selector 1d26cbab
function purgeExpiredRequest(uint256 requestId) external;
}
The interface includes functions, constants, events, and enums, as covered in the following sections.
Functions¶
The interface includes the following functions:
relayEpochIndex() - returns the current relay epoch index, where an epoch represents real time and not a block number
None.
uint256current relay epoch index
requiredDeposit() - returns the deposit required to perform a randomness request
None.
uint256required deposit amount
getRequestStatus(uint256 requestId) - returns the request status of a given randomness request
requestId- uint256 ID of the randomness request
uint8status code of the request
getRequest(uint256 requestId) - returns the request details of a given randomness request
requestId- uint256 ID of the randomness request
boolwhether the request is ready or notboolwhether the request is expired or notuint256deposit amountuint256fee amount
requestLocalVRFRandomWords(address refundAddress, uint256 fee, uint64 gasLimit, bytes32 salt, uint8 numWords, uint64 delay) - request random words generated from the parachain VRF
refundAddress- address receiving the left-over fees after the fulfillmentfee- uint256 amount to set aside to pay for the fulfillmentgasLimit- uint64 gas limit to use for the fulfillmentsalt- bytes32 string that is mixed with the randomness seed to obtain different random wordsnumWords- uint8 number of random words requested, up to the maximum number of random wordsdelay- uint64 number of blocks that must pass before the request can be fulfilled. This value will need to be between the minimum and maximum number of blocks before a local VRF request can be fulfilled
uint256ID of the created request
requestRelayBabeEpochRandomWords(address refundAddress, uint256 fee, uint64 gasLimit, bytes32 salt, uint8 numWords) - request random words generated from the relay chain BABE consensus
refundAddress- address receiving the left-over fees after the fulfillmentfee- uint256 amount to set aside to pay for the fulfillmentgasLimit- uint64 gas limit to use for the fulfillmentsalt- bytes32 string that is mixed with the randomness seed to obtain different random wordsnumWords- uint8 number of random words requested, up to the maximum number of random words
uint256ID of the created request
fulfillRequest(uint256 requestId) - fulfill the request which will call the consumer contract method fulfillRandomWords. Fees of the caller are refunded if the request is fulfillable
requestId- uint256 ID of the randomness request
None.
increaseRequestFee(uint256 requestId, uint256 feeIncrease) - increases the fee associated with a given randomness request. This is needed if the gas price increases significantly before the request is fulfilled
requestId- uint256 ID of the randomness requestfeeIncrease- uint256 amount to increase fees by
None.
purgeExpiredRequest(uint256 requestId) - removes a given expired request from storage and transfers the request fees to the caller and the deposit back to the original requester
requestId- uint256 ID of the randomness request
None.
Constants¶
The interface includes the following constants:
- maxRandomWords - the maximum number of random words being requested
- minBlockDelay - the minimum number of blocks before a request can be fulfilled for local VRF requests
- maxBlockDelay - the maximum number of blocks before a request can be fulfilled for local VRF requests
- deposit - the deposit amount needed to request random words. There is one deposit per request
| Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| MAX_RANDOM_WORDS | 100 words |
| MIN_VRF_BLOCKS_DELAY | 2 blocks |
| MAX_VRF_BLOCKS_DELAY | 2000 blocks |
| REQUEST_DEPOSIT_AMOUNT | 100 GLMR |
| Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| MAX_RANDOM_WORDS | 100 words |
| MIN_VRF_BLOCKS_DELAY | 2 blocks |
| MAX_VRF_BLOCKS_DELAY | 2000 blocks |
| REQUEST_DEPOSIT_AMOUNT | 1 MOVR |
| Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| MAX_RANDOM_WORDS | 100 words |
| MIN_VRF_BLOCKS_DELAY | 2 blocks |
| MAX_VRF_BLOCKS_DELAY | 2000 blocks |
| REQUEST_DEPOSIT_AMOUNT | 1 DEV |
Events¶
The interface includes the following events:
- FulfillmentSucceeded() - emitted when the request has been successfully executed
- FulfillmentFailed() - emitted when the request has failed to execute fulfillment
Enums¶
The interface includes the following enums:
- RequestStatus - the status of the request, which can be
DoesNotExist(0),Pending(1),Ready(2), orExpired(3) - RandomnessSource - the type of the randomness source, which can be
LocalVRF(0) orRelayBabeEpoch(1)
The Randomness Consumer Solidity Interface¶
The RandomnessConsumer.sol Solidity interface makes it easy for smart contracts to interact with the randomness precompile. Using the randomness consumer ensures the fulfillment comes from the randomness precompile.
RandomnessConsumer.sol
// SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-3.0-only
pragma solidity >=0.8.3;
/// @dev The Randomness contract's address.
address constant RANDOMNESS_ADDRESS = 0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000809;
/// @dev The Randomness contract's instance.
Randomness constant RANDOMNESS_CONTRACT = Randomness(RANDOMNESS_ADDRESS);
/// @dev Maximum number of random words being requested
uint32 constant MAX_RANDOM_WORDS = 100;
/// @dev Minimum number of blocks before a request can be fulfilled for Local VRF Request
uint32 constant MIN_VRF_BLOCKS_DELAY = 2;
/// @dev Maximum number of blocks before a request can be fulfilled for Local VRF Request
uint32 constant MAX_VRF_BLOCKS_DELAY = 2000;
/// @dev The deposit amount needed to request random words. There is 1 deposit per request
uint256 constant REQUEST_DEPOSIT_AMOUNT = 1000000000000000000;
/// @author The Moonbeam Team
/// @title Pallet Randomness Interface
/// @dev The interface through which solidity contracts will interact with Randomness
/// @custom:address 0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000809
interface Randomness {
/// @notice Event emitted when the request has been successfully executed
event FulFillmentSucceeded();
/// @notice Event emitted when the request has failed to execute fulfillment
event FulFillmentFailed();
/// @notice The status of the request
/// @param DoesNotExist The request doesn't exist
/// @param Pending The request cannot be fulfilled yet
/// @param Ready The request is ready to be fulfilled
/// @param Expired The request has expired
enum RequestStatus {
DoesNotExist,
Pending,
Ready,
Expired
}
/// @notice The type of randomness source
/// @param LocalVRF Randomness VRF using the parachain material as seed
/// @param RelayBabeEpoch Randomness VRF using relay material from previous epoch
enum RandomnessSource {
LocalVRF,
RelayBabeEpoch
}
/// @notice The request details
/// @param id The id of the request (is always < 2**64)
/// @param refundAddress The address receiving the left-over fees after the fulfillment
/// @param contractAddress The address of the contract being called back during fulfillment
/// @param fee The amount to set aside to pay for the fulfillment
/// @param gasLimit The gas limit to use for the fulfillment
/// @param salt A string being mixed with the randomness seed to obtain different random words. This should be as unique as possible; using the same salt will lead to same randomness result.
/// @param numWords The number of random words requested (from 1 to MAX_RANDOM_WORDS)
/// @param randomnessSource The type of randomness source used to generate the random words
/// @param fulfillmentBlock The parachain block number at which the request can be fulfilled (for LocalVRF only)
/// @param fulfillmentEpochIndex The relay epoch index at which the request can be fulfilled (for RelayBabeEpoch)
/// @param expirationBlock The parachain block number at which the request expires (for LocalVRF only)
/// @param expirationEpochIndex The relay epoch index at which the request expires (for RelayBabeEpoch)
/// @param status The current status of the request
struct Request {
uint256 id;
address refundAddress;
address contractAddress;
uint256 fee;
uint256 gasLimit;
bytes32 salt;
uint32 numWords;
RandomnessSource randomnessSource;
uint32 fulfillmentBlock;
uint64 fulfillmentEpochIndex;
uint32 expirationBlock;
uint64 expirationEpochIndex;
RequestStatus status;
}
/// Return the current relay epoch index
/// @dev An epoch represents real time and not a block number
/// @dev Currently, time between epoch changes cannot be longer than:
/// @dev - Kusama/Westend/Rococo: 600 relay blocks (1 hour)
/// @dev - Polkadot: 2400 relay blocks (4 hours)
/// @custom:selector 81797566
function relayEpochIndex() external view returns (uint64);
/// Return the deposit required to perform a request
/// @dev Each request will need a deposit.
/// @custom:selector fb7cfdd7
function requiredDeposit() external view returns (uint256);
/// @notice Returns the request status
/// @param requestId The id of the request to check (must be < 2**64)
/// @return status Status of the request
/// @custom:selector d8a4676f
function getRequestStatus(uint256 requestId)
external
view
returns (RequestStatus status);
/// @notice Returns the request or revert
/// @param requestId The id of the request to check (must be < 2**64)
/// @return request The request
/// @custom:selector c58343ef
function getRequest(uint256 requestId)
external
view
returns (Request memory request);
/// @notice Request random words generated from the parachain VRF
/// @dev This is using pseudo-random VRF executed by the collator at the fulfillment
/// @dev Warning:
/// @dev The collator in charge of producing the block at fulfillment can decide to skip
/// @dev producing the block in order to have a different random word generated by the next
/// @dev collator, at the cost of a block reward. It is therefore economically viable to use
/// @dev this randomness source only if the financial reward at stake is lower than the block
/// @dev reward.
/// @dev In order to reduce the risk of a collator being able to predict the random words
/// @dev when the request is performed, it is possible to increase the delay to multiple blocks
/// @dev The higher the delay is, the less likely the collator will be able to know which
/// @dev collator will be in charge of fulfilling the request.
/// @dev Fulfillment is manual and can be executed by anyone (for free) after the given delay
/// @param refundAddress The address receiving the left-over fees after the fulfillment
/// @param fee The amount to set aside to pay for the fulfillment
/// @param gasLimit The gas limit to use for the fulfillment
/// @param salt A string being mixed with the randomness seed to obtain different random words
/// @param numWords The number of random words requested (from 1 to MAX_RANDOM_WORDS)
/// @param delay The number of blocks until the request can be fulfilled (between MIN_DELAY_BLOCKS and MAX_DELAY_BLOCKS)
/// @return requestId The id of the request requestLocalVRFRandomWords
/// @custom:selector 9478430c
function requestLocalVRFRandomWords(
address refundAddress,
uint256 fee,
uint64 gasLimit,
bytes32 salt,
uint8 numWords,
uint64 delay
) external returns (uint256);
/// @notice Request random words generated from the relaychain Babe consensus
/// @dev The random words are generated from the hash of the all the VRF provided by the
/// @dev relaychain validator during 1 epoch.
/// @dev It requires a delay of at least 1 epoch after the current epoch to be unpredictable
/// @dev at the time the request is performed.
/// @dev Warning:
/// @dev The validator (on the relaychain) of the last block of an epoch can decide to skip
/// @dev producing the block in order to choose the previous generated epoch random number
/// @dev at the cost of a relaychain block rewards. It is therefore economically viable to use
/// @dev this randomness source only if the financial reward at stake is lower than the relaychain
/// @dev block reward.
/// @dev (see https://crates.parity.io/pallet_babe/struct.RandomnessFromOneEpochAgo.html)
/// @dev Fulfillment is manual and can be executed by anyone (for free) at
/// @dev the beginning of the 2nd relay epoch following the current one
/// @param refundAddress The address receiving the left-over fees after the fulfillment
/// @param fee Amount to set aside to pay for the fulfillment. Those fees are taken from the contract
/// @param gasLimit Gas limit for the fulfillment
/// @param salt Salt to be mixed with raw randomness to get output
/// @param numWords Number of random words to be returned (limited to MAX_RANDOM_WORDS)
/// @return requestId The id of the request
/// @custom:selector 33c14a63
function requestRelayBabeEpochRandomWords(
address refundAddress,
uint256 fee,
uint64 gasLimit,
bytes32 salt,
uint8 numWords
) external returns (uint256);
/// @dev fulFill the request which will call the contract method "fulfillRandomWords"
/// @dev Fees of the caller are refunded if the request is fulfillable
/// @param requestId Request to be fulfilled (must be < 2**64)
/// @custom:selector 9a91eb0d
function fulfillRequest(uint256 requestId) external;
/// @param requestId Request receiving the additional fees (must be < 2**64)
/// @param feeIncrease Amount to increase
/// @custom:selector d0408a7f
function increaseRequestFee(uint256 requestId, uint256 feeIncrease)
external;
/// @param requestId Request to be purged (must be < 2**64)
/// @custom:selector 1d26cbab
function purgeExpiredRequest(uint256 requestId) external;
}
The consumer interface includes the following functions:
- fulfillRandomWords(uint256 requestId, uint256[] memory randomWords) - handles the VRF response for a given request. This method is triggered by a call to
rawFulfillRandomWords - rawFulfillRandomWords(uint256 requestId, uint256[] memory randomWords) - executed when the
fulfillRequestfunction of the randomness precompile is called. The origin of the call is validated, ensuring the randomness precompile is the origin, and then thefulfillRandomWordsmethod is called
Request & Fulfill Process¶
To consume randomness, you must have a contract that does the following:
- Imports the
Randomness.solprecompile andRandomnessConsumer.solinterface - Inherits from the
RandomnessConsumer.solinterface - Requests randomness through the precompile's
requestLocalVRFRandomWordsmethod orrequestRelayBabeEpochRandomWordsmethod, depending on the source of randomness you want to use - Requests fulfillment through the precompile's
fulfillRequestmethod - Consumes randomness through a
fulfillRandomWordsmethod with the same signature as thefulfillRandomWordsmethod of theRandomnessConsumer.solcontract
When randomness is requested through the precompile's requestLocalVRFRandomWords or requestRelayBabeEpochRandomWords method, a fee is set aside to pay for the fulfillment of the request. When using local VRF, to increase unpredictability, a specified delay period (in blocks) must pass before the request can be fulfilled. At the very least, the delay period must be greater than one block. For BABE epoch randomness, you do not need to specify a delay but can fulfill the request at the beginning of the 2nd epoch following the current one.
After the delay, fulfillment of the request can be manually executed by anyone through the fulfillRequest method using the fee that was initially set aside for the request.
When fulfilling the randomness request via the precompile's fulfillRequest method, the rawFulfillRandomWords function in the RandomnessConsumer.sol contract will be called, which will verify that the sender is the randomness precompile. From there, fulfillRandomWords is called and the requested number of random words are computed using the current block's randomness result and a given salt and returned. If the fulfillment was successful, the FulfillmentSucceeded event will be emitted; otherwise the FulfillmentFailed event will be emitted.
For fulfilled requests, the cost of execution will be refunded from the request fee to the caller of fulfillRequest. Then any excess fees and the request deposit are transferred to the specified refund address.
Your contract's fulfillRandomWords callback is responsible for handling the fulfillment. For example, in a lottery contract, the callback would use the random words to choose a winner and payout the winnings.
If a request expires it can be purged through the precompile's purgeExpiredRequest function. When this function is called the request fee is paid out to the caller and the deposit will be returned to the original requester.
The happy path for a randomness request is shown in the following diagram:
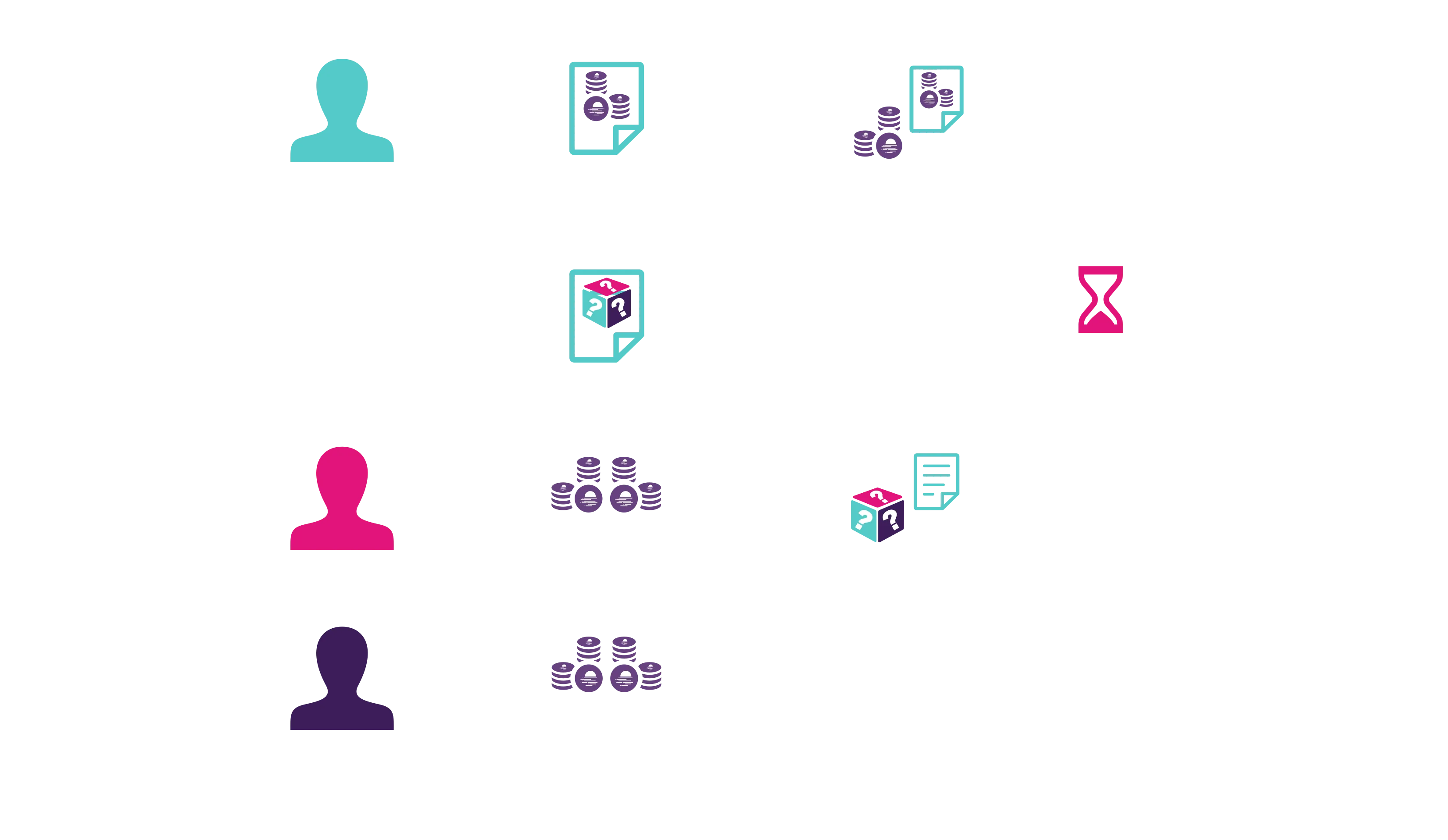
Generate a Random Number using the Randomness Precompile¶
In the following sections of this tutorial, you'll learn how to create a smart contract that generates a random number using the Randomness Precompile and the Randomness Consumer. If you want to just explore some of the functions of the Randomness Precompile, you can skip ahead to the Use Remix to Interact Directly with the Randomness Precompile section.
Checking Prerequisites¶
For this guide, you will need to have the following:
- MetaMask installed and connected to Moonbase Alpha
- An account funded with DEV tokens. You can get DEV tokens for testing on Moonbase Alpha once every 24 hours from the Moonbase Alpha Faucet
Create a Random Number Generator Contract¶
The contract that will be created in this section includes the functions that you'll need at a bare minimum to request randomness and consume the results from fulfilling randomness requests.
This contract is for educational purposes only and is not meant for production use.
The contract will include the following functions:
- A constructor that accepts the deposit required to request randomness
- A function that submits randomness requests. For this example, the source of randomness will be local VRF, but you can easily modify the contract to use BABE epoch randomness
- A function that fulfills the request by calling the
fulfillRequestfunction of the Randomness Precompile. This function will bepayableas the fulfillment fee will need to be submitted at the time of the randomness request - A function that consumes the fulfillment results. This function's signature must match the signature of the
fulfillRandomWordsmethod of the Randomness Consumer contract
Without further ado, the contract is as follows:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-3.0-only
pragma solidity >=0.8.0;
import "https://github.com/moonbeam-foundation/moonbeam/blob/master/precompiles/randomness/Randomness.sol";
import {RandomnessConsumer} from "https://github.com/moonbeam-foundation/moonbeam/blob/master/precompiles/randomness/RandomnessConsumer.sol";
contract RandomNumber is RandomnessConsumer {
// The Randomness Precompile Interface
Randomness public randomness =
Randomness(0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000809);
// Variables required for randomness requests
uint256 public requiredDeposit = randomness.requiredDeposit();
uint64 public FULFILLMENT_GAS_LIMIT = 100000;
// The fee can be set to any value as long as it is enough to cover
// the fulfillment costs. Any leftover fees will be refunded to the
// refund address specified in the requestRandomness function below.
// 150 Gwei should be sufficient for all networks.
// For Moonbase Alpha and Moonriver, you can specify 5 Gwei
uint256 public MIN_FEE = FULFILLMENT_GAS_LIMIT * 150 gwei;
uint32 public VRF_BLOCKS_DELAY = MIN_VRF_BLOCKS_DELAY;
bytes32 public SALT_PREFIX = "INSERT_ANY_STRING_FOR_SALT";
// Storage variables for the current request
uint256 public requestId;
uint256[] public random;
constructor() payable RandomnessConsumer() {
// Because this contract can only perform 1 random request at a time,
// We only need to have 1 required deposit
require(msg.value >= requiredDeposit);
}
function requestRandomness() public payable {
// Make sure that the value sent is enough
require(msg.value >= MIN_FEE);
// Request local VRF randomness
requestId = randomness.requestLocalVRFRandomWords(
msg.sender, // Refund address
msg.value, // Fulfillment fee
FULFILLMENT_GAS_LIMIT, // Gas limit for the fulfillment
SALT_PREFIX ^ bytes32(requestId++), // A salt to generate unique results
1, // Number of random words
VRF_BLOCKS_DELAY // Delay before request can be fulfilled
);
}
function fulfillRequest() public {
randomness.fulfillRequest(requestId);
}
function fulfillRandomWords(
uint256, // requestId
uint256[] memory randomWords
) internal override {
// Save the randomness results
random = randomWords;
}
}
As you can see, there are also some constants in the contract that can be edited as you see fit, especially the SALT_PREFIX which can be used to produce unique results.
In the following sections, you'll use Remix to deploy and interact with the contract.
Remix Set Up¶
To add the contract to Remix and follow along with this section of the tutorial, you will need to create a new file named RandomnessNumber.sol in Remix and paste the RandomNumber contract into the file.
Compile & Deploy the Random Number Generator Contract¶
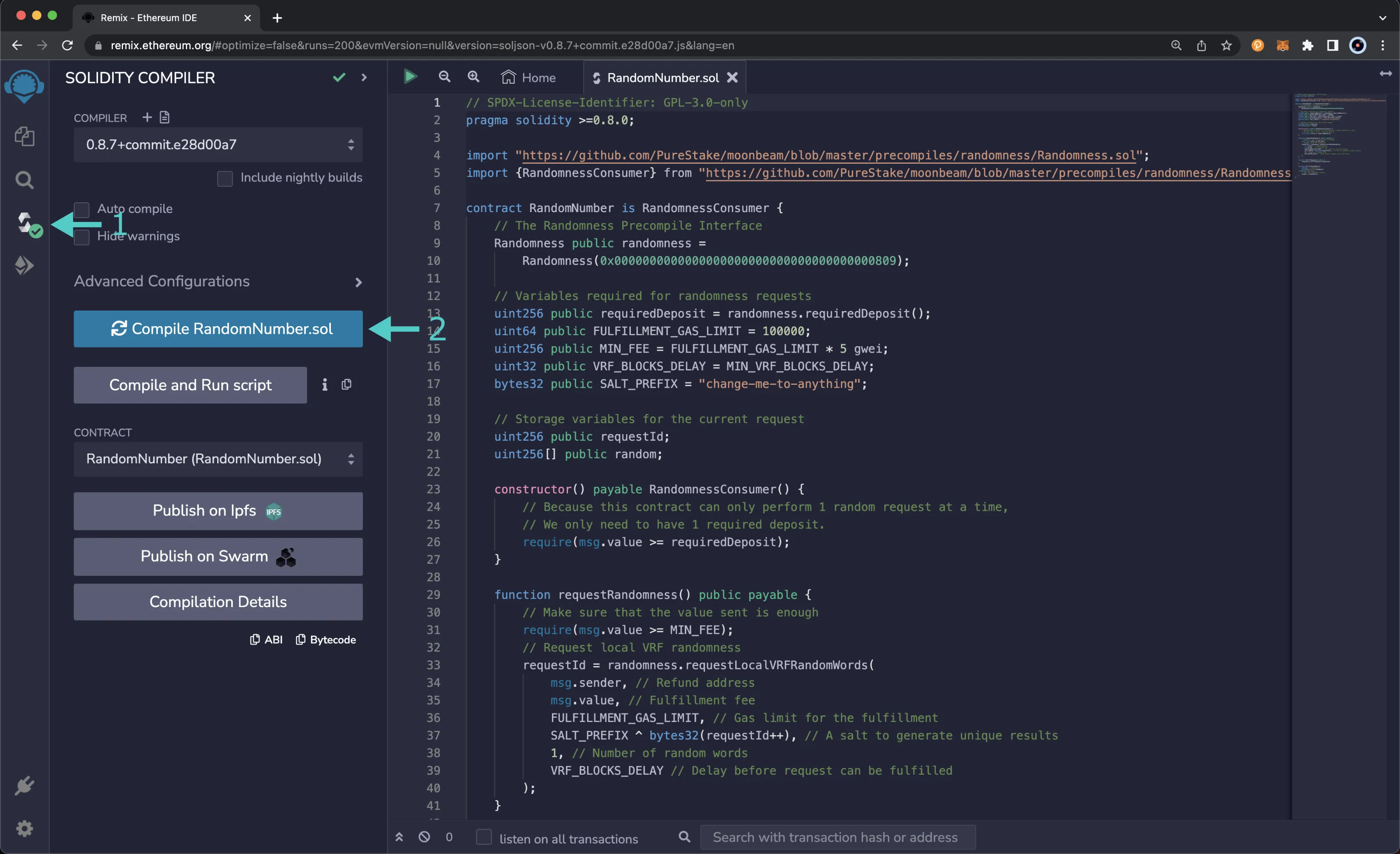
To compile the RandomNumber.sol contract in Remix, you'll need to take the following steps:
- Click on the Compile tab, second from top
- Click on the Compile RandomNumber.sol button
If the contract was compiled successfully, you will see a green checkmark next to the Compile tab.
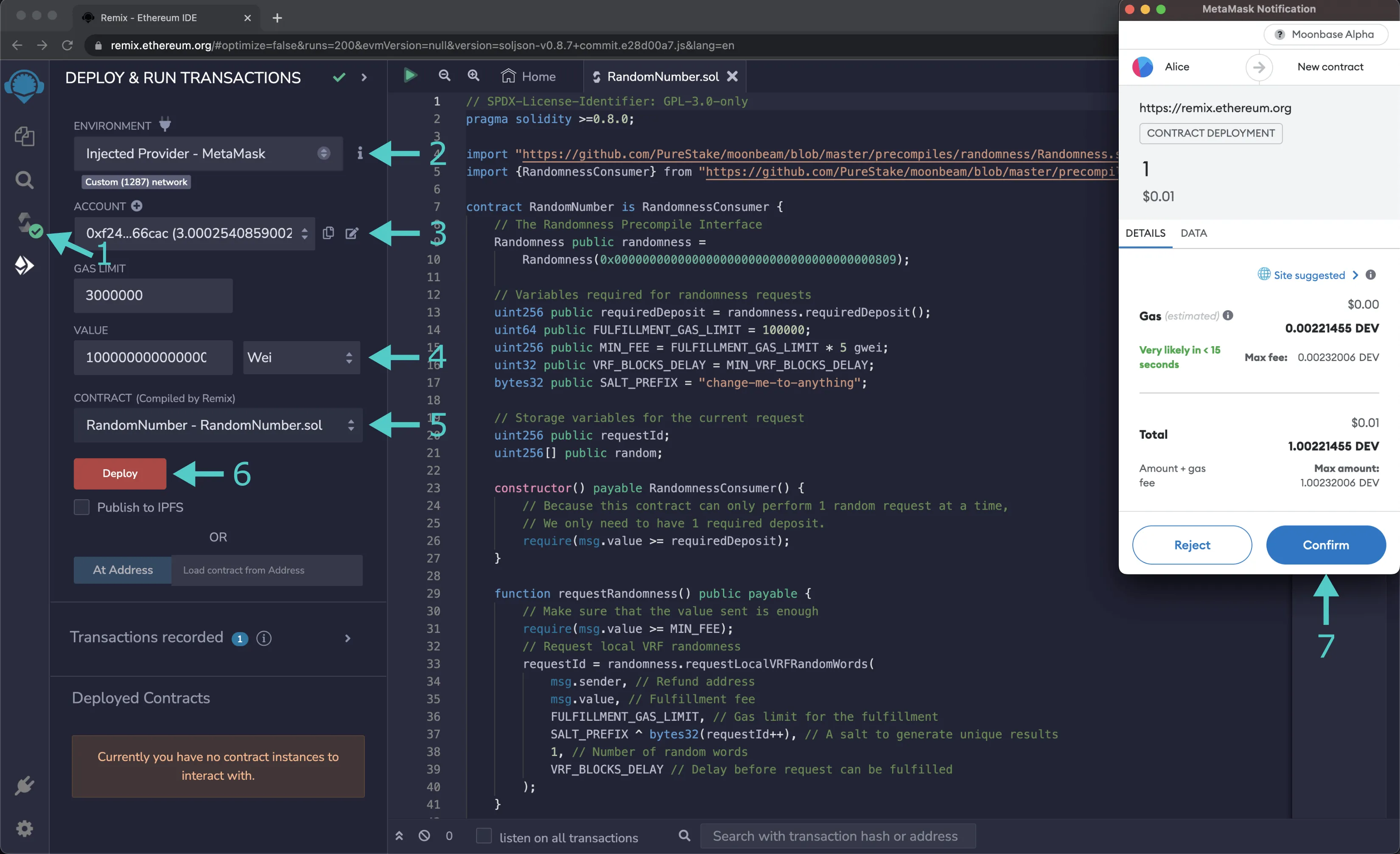
Now you can go ahead and deploy the contract by taking these steps:
- Click on the Deploy and Run tab directly below the Compile tab
- Make sure Injected Provider - Metamask is selected in the ENVIRONMENT dropdown. Once you select Injected Provider - Metamask, you might be prompted by MetaMask to connect your account to Remix
- Make sure the correct account is displayed under ACCOUNT
- Enter the deposit amount in the VALUE field, which is
1000000000000000000in Wei (1Ether) - Ensure RandomNumber - RandomNumber.sol is selected in the CONTRACT dropdown
- Click Deploy
- Confirm the MetaMask transaction that appears by clicking Confirm
The RANDOMNUMBER contract will appear in the list of Deployed Contracts.
Submit a Request to Generate a Random Number¶
To request randomness, you're going to use the requestRandomness function of the contract, which will require you to submit a deposit as defined in the Randomness Precompile. You can submit the randomness request and pay the deposit by taking these steps:
- Enter an amount in the VALUE field for the fulfillment fee, it must be equal to or greater than the minimum fee specified in the
RandomNumbercontract, which is15000000Gwei. - Expand the RANDOMNUMBER contract
- Click on the requestRandomness button
- Confrm the transaction in MetaMask
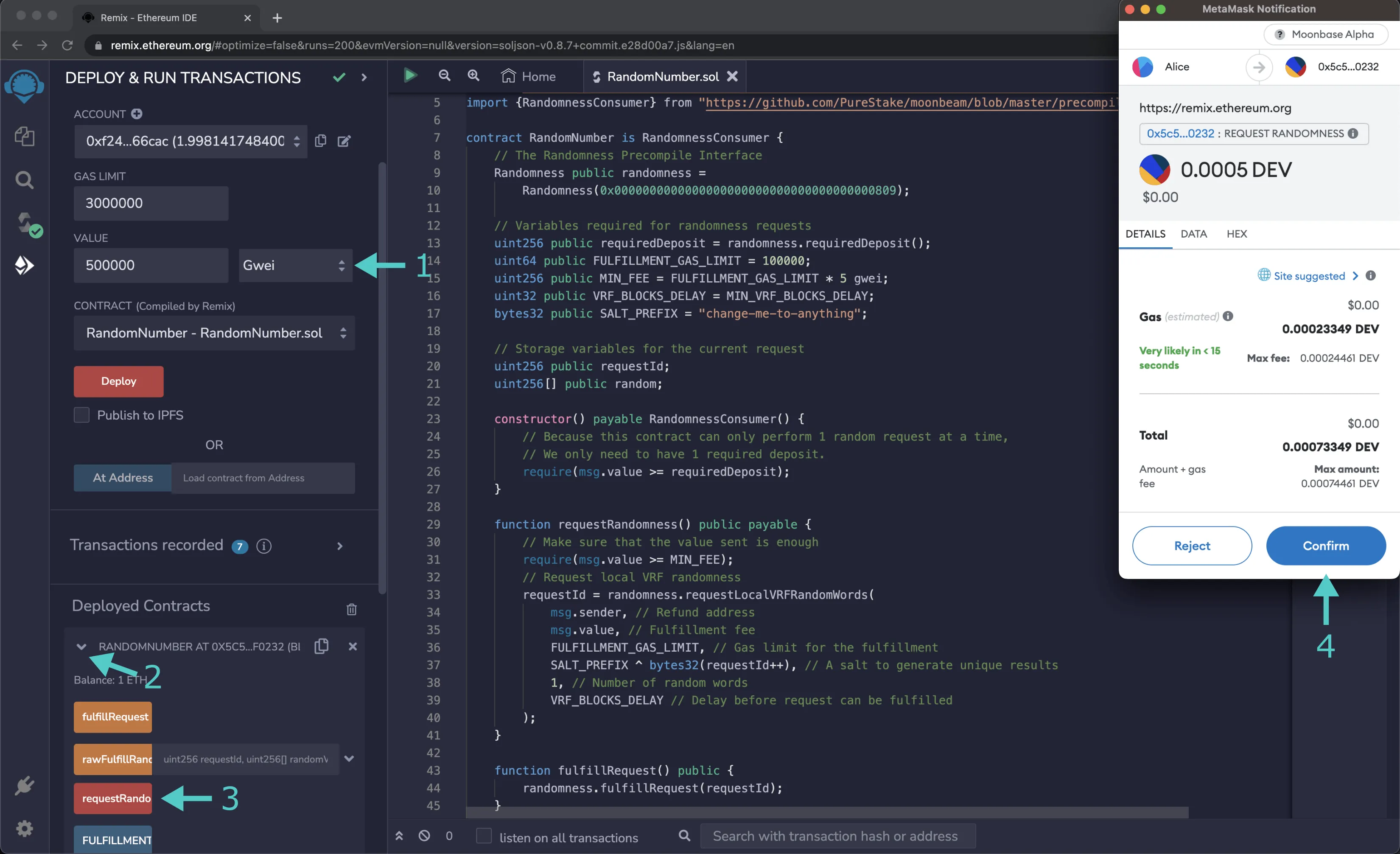
Once you submit the transaction, the requestId will be updated with the ID of the request. You can use the requestId call of the Random Number contract to get the request ID and the getRequestStatus function of the Randomness Precompile to check the status of this request ID.
Fulfill the Request and Save the Random Number¶
After submitting the randomness request, you'll need to wait for the duration of the delay before you can fulfill the request. For the RandomNumber.sol contract, the delay was set to the minimum block delay defined in the Randomness Precompile, which is 2 blocks. You must also fulfill the request before it is too late. For local VRF, the request expires after 10000 blocks and for BABE epoch randomness, the request expires after 10000 epochs.
Assuming you've waited for the minimum blocks (or epochs if you're using BABE epoch randomness) to pass and the request hasn't expired, you can fulfill the request by taking the following steps:
- Click on the fulfillRequest button
- Confirming the transaction in MetaMask
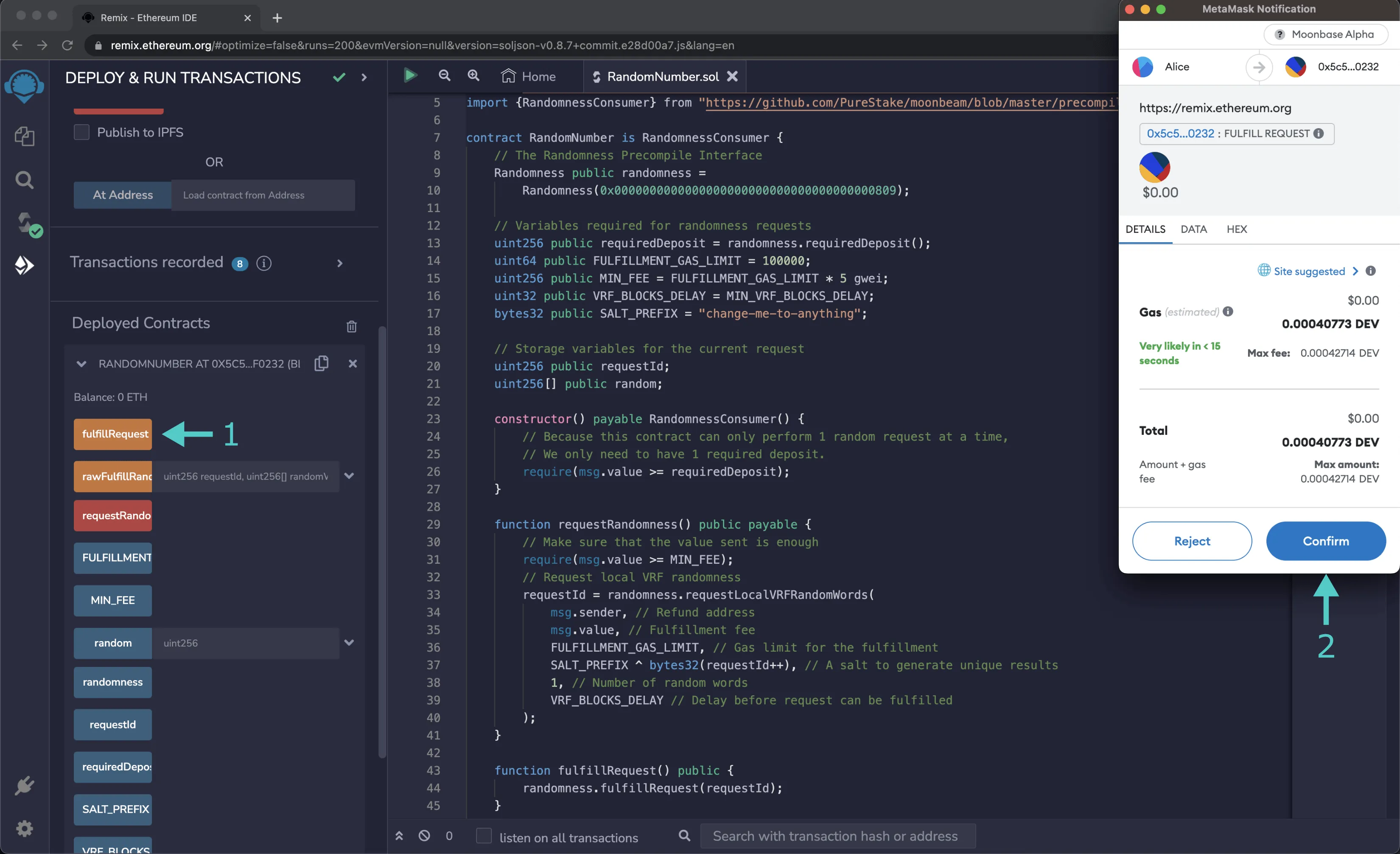
Once the request has been fulfilled, you can check the random number that was generated:
- Expand the random function
- Since the contract only requested one random word, you can get the random number by accessing the
0index of therandomarray - Click call
- The random number will appear below the call button
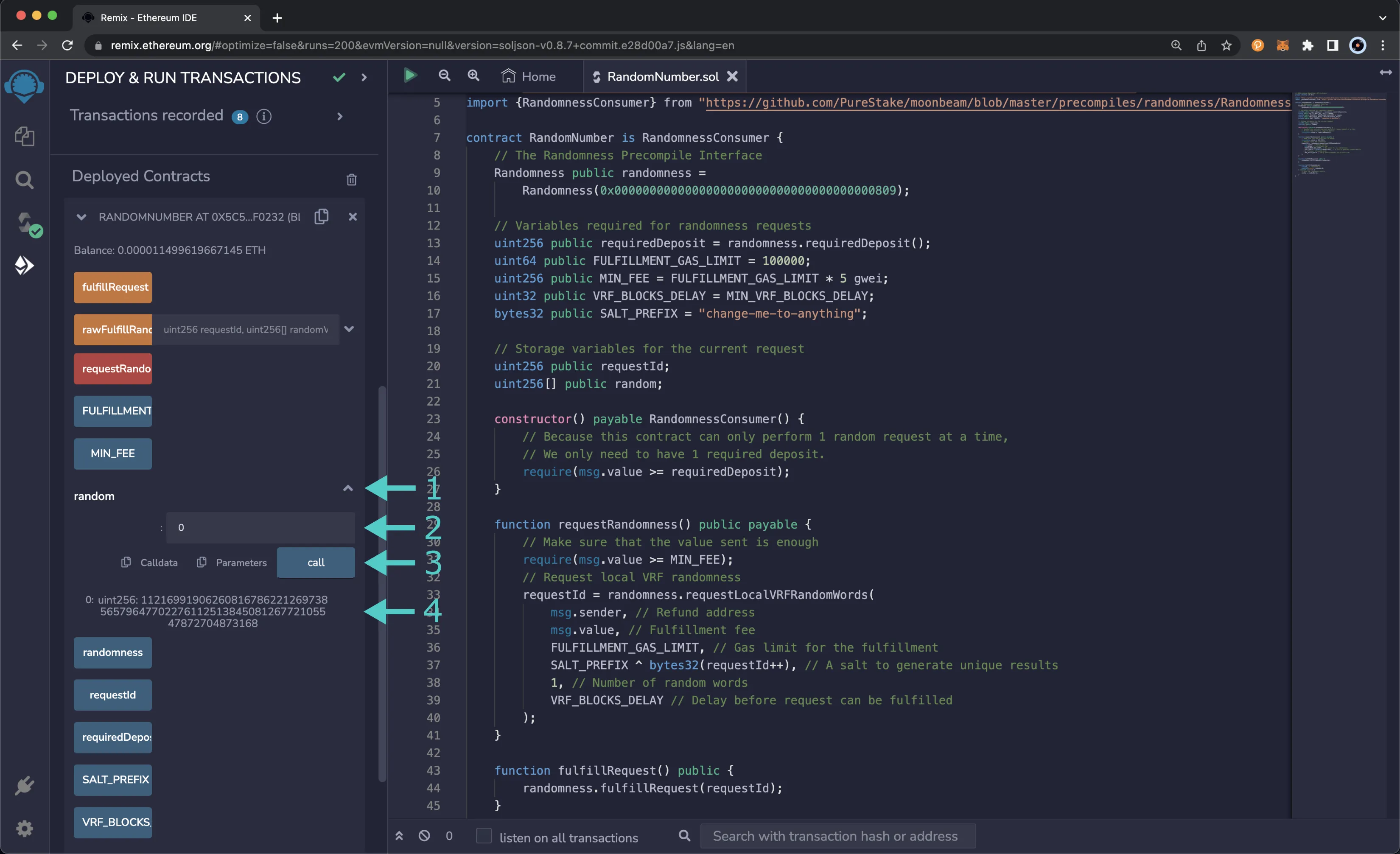
Upon successful fulfillment, the excess fees and deposit will be sent to the address specified as the refund address.
If the request happened to expire before it could be fulfilled, you can interact with the Randomness Precompile directly to purge the request and unlock the deposit and fees. Please refer to the following section for instructions on how to do this.
Use Remix to Interact Directly with the Randomness Precompile¶
In addition to interacting with the randomness precompile via a smart contract, you can also interact with it directly in Remix to perform operations such as creating a randomness request, checking on the status of a request, and purging expired requests. Remember, you need to have a contract that inherits from the consumer contract in order to fulfill requests, as such if you fulfill a request using the precompile directly there will be no way to consume the results.
Remix Set Up¶
To add the interfaces to Remix and follow along with this section of the tutorial, you will need to:
- Get a copy of
Randomness.sol - Paste the file contents into a Remix file named Randomness.sol
Compile & Access the Randomness Precompile¶
Next, you will need to compile the Randomness.sol file in Remix. To get started, make sure you have the Randomness.sol file open and take the following steps:
- Click on the Compile tab, second from top
- To compile the contract, click on Compile Randomness.sol
If the contract was compiled successfully, you will see a green checkmark next to the Compile tab.
Instead of deploying the randomness precompile, you will access the interface given the address of the precompiled contract:
- Click on the Deploy and Run tab directly below the Compile tab in Remix. Please note the precompiled contract is already deployed
- Make sure Injected Provider - Metamask is selected in the ENVIRONMENT dropdown. Once selected, you might be prompted by MetaMask to connect your account to Remix
- Make sure the correct account is displayed under ACCOUNT
- Ensure Randomness - Randomness.sol is selected in the CONTRACT dropdown. Since this is a precompiled contract, there is no need to deploy any code. Instead we are going to provide the address of the precompile in the At Address Field
- Provide the address of the batch precompile:
0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000809and click At Address
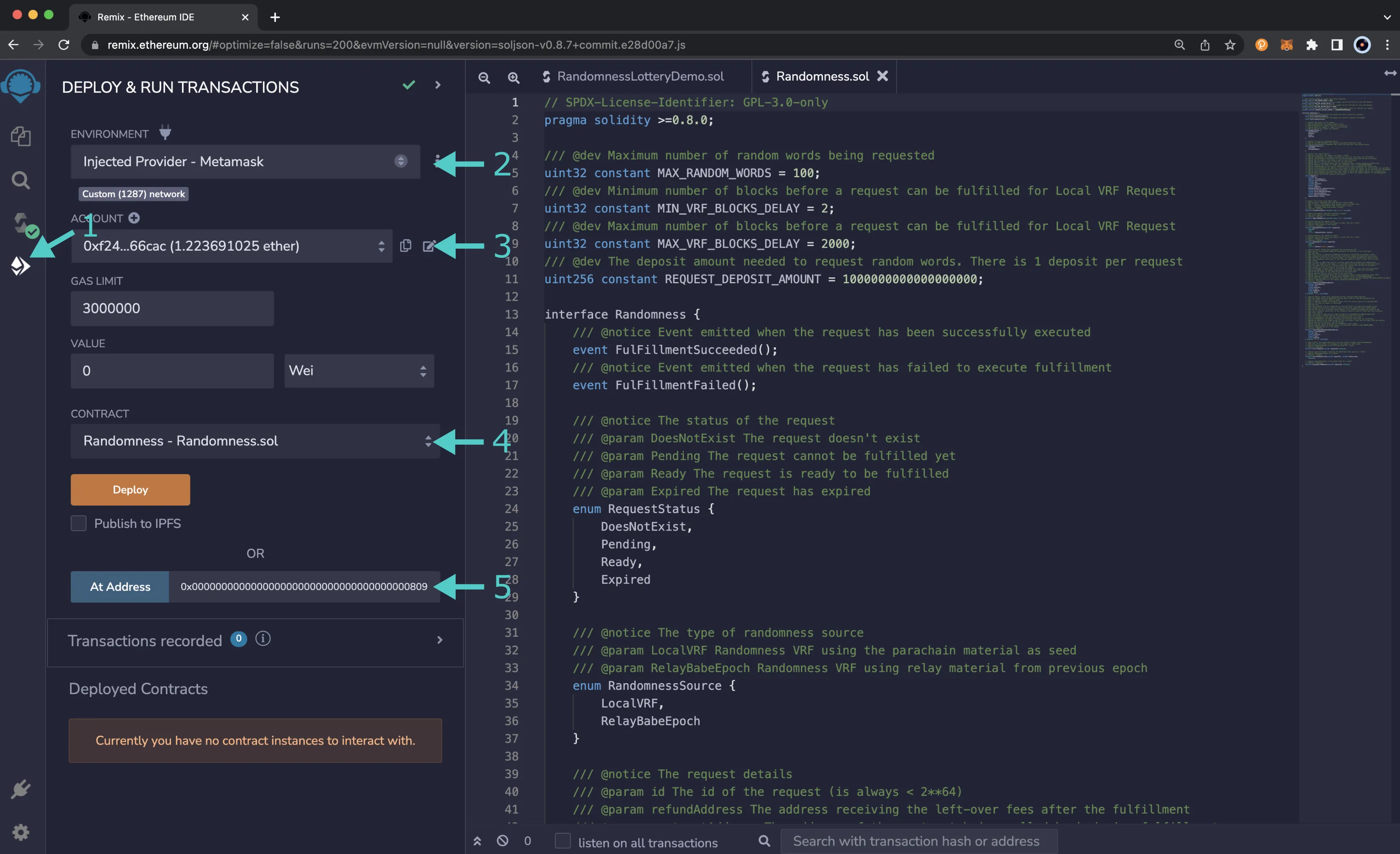
The RANDOMNESS precompile will appear in the list of Deployed Contracts. You will use this to fulfill the randomness request made from the lottery contract later on in this tutorial.
Get Request Status & Purge Expired Request¶
Anyone can purge expired requests. You do not need to be the one who requested the randomness to be able to purge it. When you purge an expired request, the request fees will be transferred to you, and the deposit for the request will be returned to the original requester.
To purge a request, first you have to make sure that the request has expired. To do so, you can verify the status of a request using the getRequestStatus function of the precompile. The number that is returned from this call corresponds to the index of the value in the RequestStatus enum. As a result, you'll want to verify the number returned is 3 for Expired.
Once you've verified that the request is expired, you can call the purgeExpiredRequest function to purge the request.
To verify and purge a request, you can take the following steps:
- Expand the RANDOMNESS contract
- Enter the request ID of the request you want to verify has expired and click on getRequestStatus
- The response will appear just underneath the function. Verify that you received a
3 - Expand the purgeExpiredRequest function and enter the request ID
- Click on transact
- MetaMask will pop-up and you can confirm the transaction
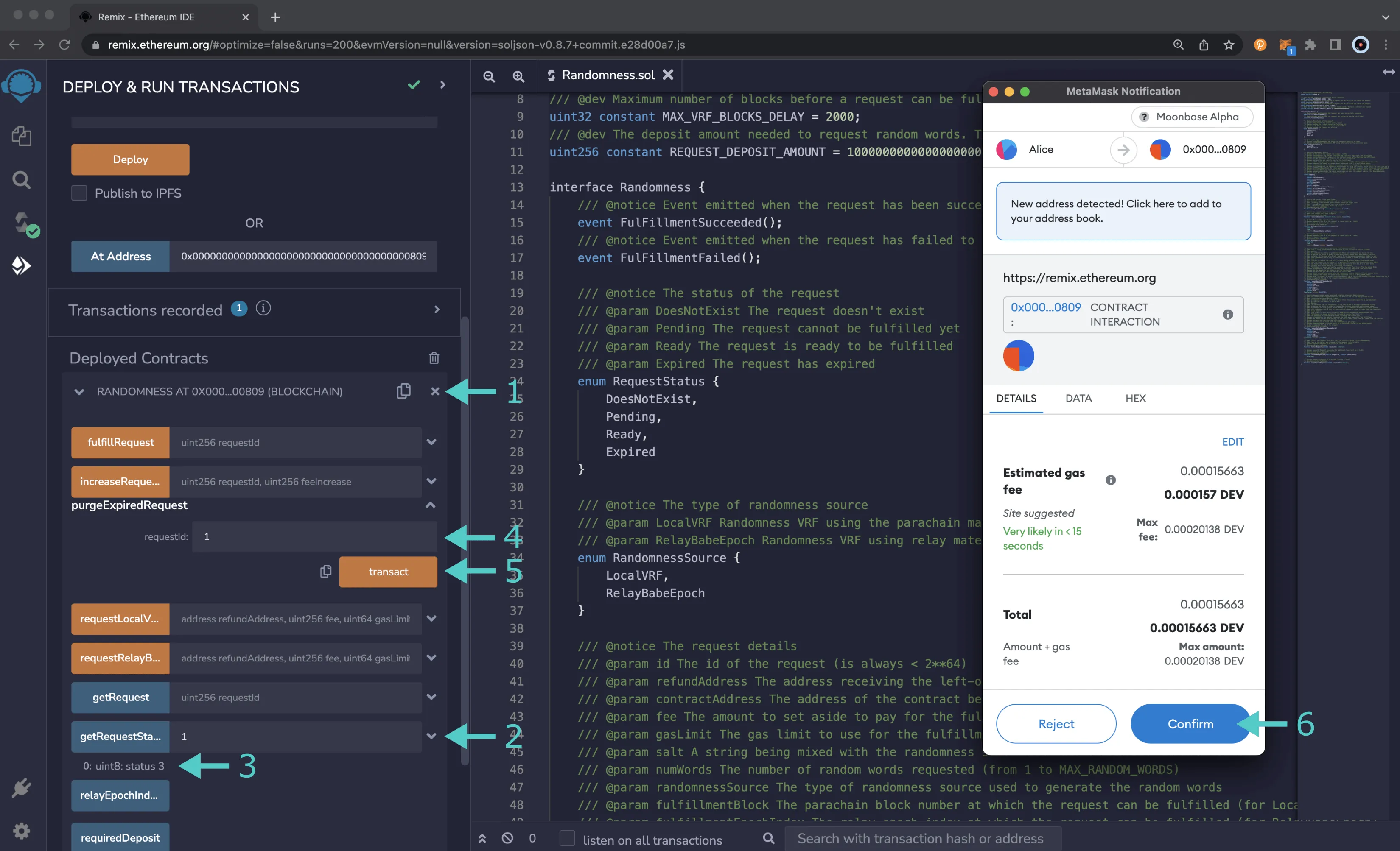
Once the transaction goes through, you can verify the request has been purged by calling the getRequestStatus function again with the same request ID. You should receive a status of 0, or DoesNotExist. You can also expect the amount of the request fees to be transferred to your account.
| Created: August 12, 2022