Moonbeam Routed Liquidity¶
Introduction¶
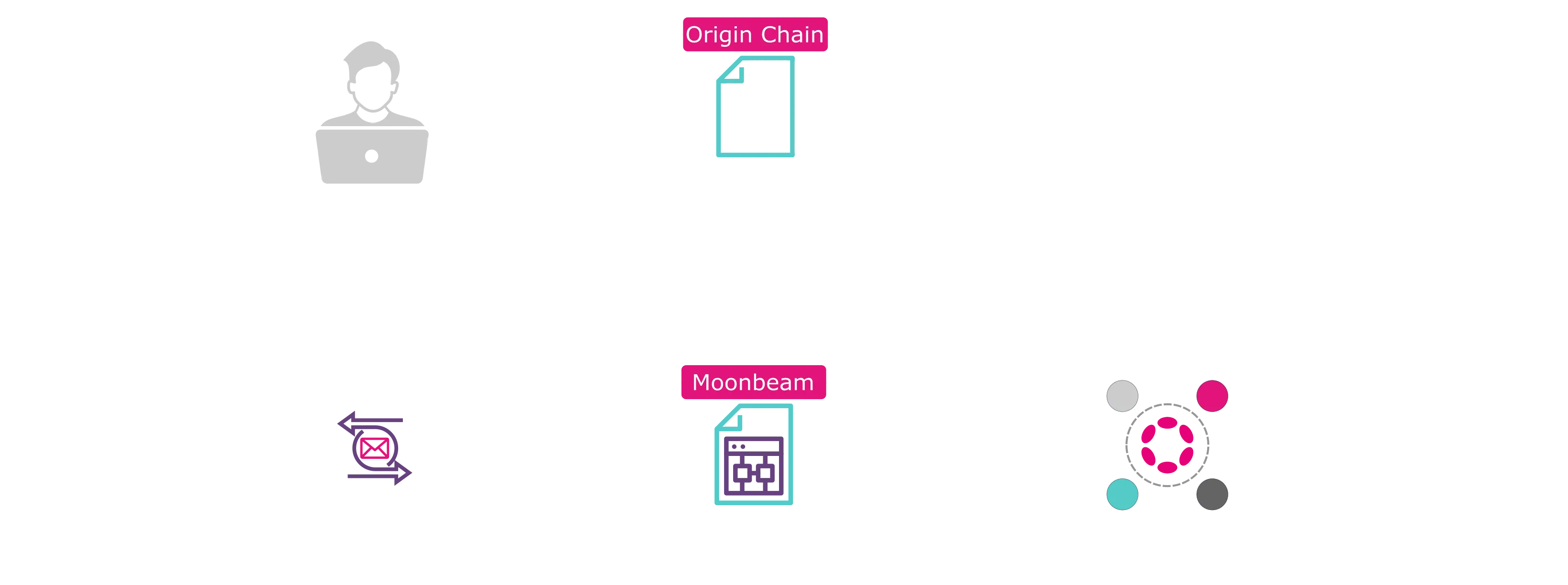
Moonbeam Routed Liquidity (MRL) refers to a use case in which liquidity in any blockchain ecosystem that Moonbeam is connected to can be routed to Polkadot parachains. This is possible because of multiple components that work together:
- General Message Passing (GMP) - technology connecting multiple blockchains, including Moonbeam. With it, developers can pass messages with arbitrary data, and tokens can be sent across non-parachain blockchains through chain-agnostic GMP protocols
- Cross-Consensus Message Passing (XCM) - Polkadot's flavor of GMP. Main technology driving cross-chain interactions between Polkadot and its parachains, including Moonbeam
- XCM-Enabled ERC-20s - also referred to as local XC-20s, are all of the ERC-20 tokens that exist on Moonbeam's EVM that are XCM-enabled out of the box
- GMP Precompile - a precompiled contract that acts as an interface between a message passed from Wormhole GMP protocol and XCM
These components are combined to offer seamless liquidity routing into parachains through Moonbeam. Liquidity can be routed to parachains using either the GMP Precompile or traditional smart contracts that interact with XCM-related precompiles, like the X-Tokens Precompile.
GMP protocols typically move assets in a lock/mint or burn/mint fashion. This liquidity exists on Moonbeam normally as ERC-20 tokens. All ERC-20s on Moonbeam are now XCM-enabled, meaning they can now exist as XC-20s in any other parachain, as long as they are registered on the other parachain. XCM-enabled ERC-20s are referred to as local XC-20s on Moonbeam.
MRL is currently available through Wormhole-connected chains, but nothing stops a parachain team from implementing a similar pathway through a different GMP provider.
This guide will primarily cover the process of integrating with Wormhole's SDKs and interfaces so that your parachain can access liquidity from non-parachain blockchains through Moonbeam. It will also cover the requirements to get started and the tokens available through Wormhole.
Prerequisites¶
To begin an MRL integration with your parachain, you will first need to:
- Establish a cross-chain integration with Moonbeam via HRMP channels so assets can be sent from Moonbeam to your parachain
- Register Moonbeam’s asset on your parachain. This is required due to a temporary drawback of pallets that send XCM messages for asset transfer, making Moonbeam’s native gas asset the only asset that can be used as a cross-chain fee on the way back
- Register the local XC-20 token(s) you want routed to your parachain
- Allow these local XC-20 token(s) to be used for XCM fees
- Allow users to send the
TransactXCM instruction (viapolkadotXcm.Sendor with the XCM Transactor Pallet), which enables remote EVM calls, allowing accounts on a remote parachain to interact with the bridging smart contracts on Moonbeam
MRL Through Wormhole¶
While MRL intends to encompass many different GMP providers, Wormhole is the first built for the public.After you have completed all of the prerequisites, to receive liquidity through Wormhole, you'll need to:
- Notify the Moonbeam team of your desire to integrate into the MRL program so that we can help you with the technical implementation
- Connect with the Wormhole team and other MRL-dependent frontends to finalize technical details and sync announcements. They will likely need the following information:
- Parachain ID
- The account type that your parachain uses (i.e., AccountId32 or AccountKey20)
- The addresses and names of the tokens that you have registered
- An endpoint that a Wormhole Connect frontend can use
- Why do you want your parachain to be connected through Wormhole Connect?
Send Tokens Through Wormhole to a Parachain¶
MRL provides a one-click solution that allows you to define a multilocation as the final destination for your assets arriving from any Wormhole chain with a Wormhole Connect integration.
To send tokens through Wormhole and MRL, user interfaces will use a mixture of the Wormhole TokenBridge and Moonbeam’s GMP Precompile.
Users transferring liquidity will invoke the transferTokensWithPayload method on the origin chain's deployment of the Wormhole TokenBridge smart contract, which implements the ITokenBridge.sol interface to send tokens to the GMP Precompile. This function requires a bytes payload, formatted as a SCALE-encoded multilocation object wrapped within another precompile-specific versioned type. To learn how to build this payload, please refer to the Building the Payload for Wormhole section of the GMP Precompile documentation.
Wormhole relies on a set of distributed nodes that monitor the state on several blockchains. In Wormhole, these nodes are referred to as Guardians. The Guardian's role is to observe messages and sign the corresponding payloads. If 2/3rds of Wormhole's signing Guardians validate a particular message, the message becomes approved and can be received on other chains.
The Guardian signatures and the message form a proof called a Verified Action Approval (VAA). These VAAs are delivered to their destinations by relayers within the Wormhole network. On the destination chain, the VAA is used to perform an action. In this case, the VAA is passed into the wormholeTransferERC20 function of the GMP Precompile, which processes the VAA through the Wormhole bridge contract (which mints the tokens) and relays the tokens to a parachain using XCM messages. Please note that as a parachain integrating MRL, you will likely not need to implement or use the GMP Precompile.
A relayer's only job is to pass the transactions approved by Wormhole Guardians to the destination chain. MRL is supported by some relayers already, but anyone can run one. Furthermore, users can manually execute their transaction in the destination chain when bridging through Wormhole and avoid relayers altogether.
Send Tokens From a Parachain Back Through Wormhole¶
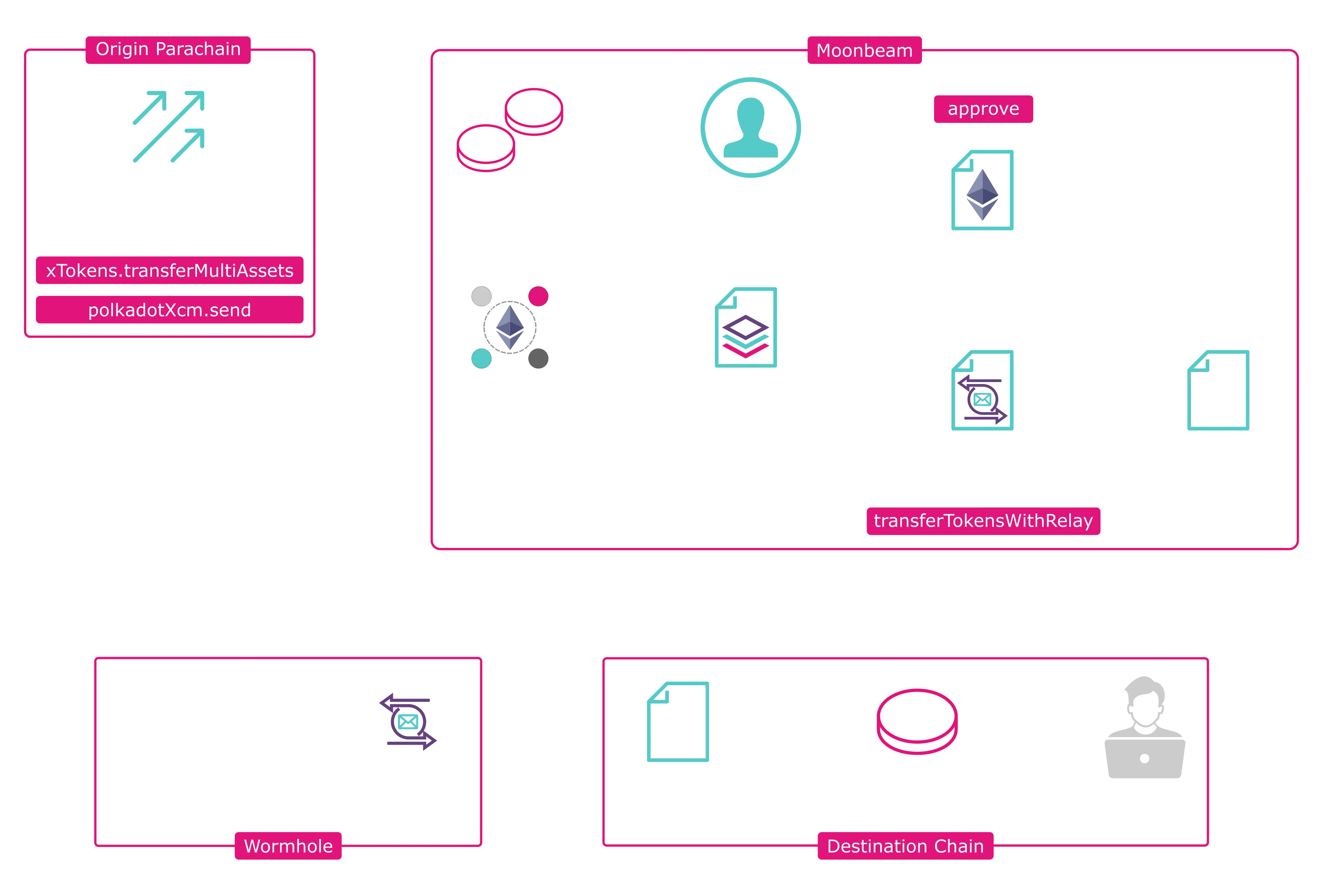
To send tokens from a parachain back through Wormhole to a destination chain, a user must send a transaction, preferably using the utility.batchAll extrinsic, which will batch a token transfer and a remote execution action into a single transaction. For example, a batch with a xTokens.transferMultiassets call and a polkadotXcm.send call with the Transact instruction.
The reason for batching is to offer a one-click solution. Nevertheless, for now, the user must also own xcGLMR (representation of GLMR) on the parachain. There are two main reasons as to why:
- Local XC-20s (XCM-enabled ERC-20s) can't be used to pay for XCM execution on Moonbeam. This was a design decision, as it was preferred to treat them as ERC-20s and utilize the native
transferfunction of the ERC-20 interface. Consequently, XCM instructions handling the XC-20s are only limited to moving funds from one account to another and don't understand the Holding Register that is inherent to the XCM flow - Currently, XCM-related pallets limit XCM messages' ability to send tokens with different reserve chains. Consequently, you can't send an XC-20 and set the fee token to be the native parachain token
Note that as of late 2024, the X-Tokens precompile now uses the Polkadot XCM pallet under the hood, replacing the X-Tokens pallet. Parachains using a different pallet must implement their own solution to transfer reserve and non-reserve assets in a single message.
As an example, a brief overview of the entire process of sending MRL tokens from a parachain back through Wormhole to a destination chain is as follows:
- Send a batch transaction using the
batchAllextrinsic of the Utility pallet that contains the following two calls.xTokens.transferMultiassets- sends xcGLMR and the local XC-20 to the user’s Computed Origin account. The Computed Origin account is a keyless account on Moonbeam that an account on another parachain has control of via XCMpolkadotXcm.send- with theTransactinstruction. Sends a remote EVM call via XCM to the Batch Precompile on Moonbeam, which batches the following two calls into a single remote EVM transaction using theethereumXcm.transactextrinsic:approve(of the local XC-20 contract) - approves the Wormhole relayer to transfer the local XC-20transferTokensWithRelay(of the relayer contract) - calls thetransferTokensWithPayloadfunction of the Wormhole TokenBridge smart contract on Moonbeam to transfer the tokens cross-chain, which broadcasts the message for the Wormhole Guardians to pick up
- The Guardian Network will pick up on the Wormhole transaction and sign it
- A Wormhole relayer will relay the tokens to the destination chain and destination account
Now that you have a general idea of the game plan, you can begin implementing it. The example in this guide will show you how to transfer assets from a parachain to Moonbase Alpha and back through Wormhole to the destination chain, but this guide can be adapted for Moonbeam.
Calculate the Computed Origin Account¶
To send tokens back through Wormhole, you'll need to calculate the user's Computed Origin account (previously referred to as a multilocation-derivative account) on Moonbeam. This can be done off-chain using the calculate-multilocation-derivative-account.ts script from the xcm-tools repository. For more details, you can refer to the Computed Origins guide.
Alternatively, the multilocationToAddress function of the XCM Utilities Precompile can also be used.
Create a Project¶
You'll need to create a new project directory for the files you'll be building in this guide. Take the following steps to set up your project:
-
Create a new directory and change into the directory
mkdir wormhole-mrl-demo && cd wormhole-mrl-demo -
Create a
package.jsonfile:npm init -y -
Install packages that you'll need to build the remote EVM calls and the XCM extrinsics
npm i @polkadot/api ethers -
Create the files that you'll need for this guide:
build-transfer-multiassets-call.js- for creating thexTokens.transferMultiassetsextrinsic that transfers assets cross-chain. This contains the logic for the first call of the batch transactionbuild-remote-calldata.js- for creating the encoded calldata that approves the Wormhole relayer to transfer the local XC-20 and initiates the transfer via the Wormhole TokenBridge contract. This is required for the second call of the batch transactionbuild-remote-evm-call.js- to create thepolkadotXcm.sendextrinsic that executes the remote EVM call. This contains the logic for the second call of the batch transactionsend-batch-transaction.js- for assembling and sending the batch transaction for the asset transfer and the remote EVM call
touch build-transfer-multiassets.js build-remote-calldata.js \ build-remote-evm-call.js send-batch-transaction.js -
Create a directory and files for the ABIs of each of the contracts you'll be working within this guide:
mkdir abi && touch abi/ERC20.js abi/TokenRelayer.js abi/Batch.jsERC-20 Interface ABI
ERC20.jsexport default [ { anonymous: false, inputs: [ { indexed: true, internalType: 'address', name: 'owner', type: 'address', }, { indexed: true, internalType: 'address', name: 'spender', type: 'address', }, { indexed: false, internalType: 'uint256', name: 'value', type: 'uint256', }, ], name: 'Approval', type: 'event', }, { anonymous: false, inputs: [ { indexed: true, internalType: 'address', name: 'from', type: 'address', }, { indexed: true, internalType: 'address', name: 'to', type: 'address', }, { indexed: false, internalType: 'uint256', name: 'value', type: 'uint256', }, ], name: 'Transfer', type: 'event', }, { inputs: [ { internalType: 'address', name: 'owner', type: 'address', }, { internalType: 'address', name: 'spender', type: 'address', }, ], name: 'allowance', outputs: [ { internalType: 'uint256', name: '', type: 'uint256', }, ], stateMutability: 'view', type: 'function', }, { inputs: [ { internalType: 'address', name: 'spender', type: 'address', }, { internalType: 'uint256', name: 'amount', type: 'uint256', }, ], name: 'approve', outputs: [ { internalType: 'bool', name: '', type: 'bool', }, ], stateMutability: 'nonpayable', type: 'function', }, { inputs: [ { internalType: 'address', name: 'account', type: 'address', }, ], name: 'balanceOf', outputs: [ { internalType: 'uint256', name: '', type: 'uint256', }, ], stateMutability: 'view', type: 'function', }, { inputs: [], name: 'totalSupply', outputs: [ { internalType: 'uint256', name: '', type: 'uint256', }, ], stateMutability: 'view', type: 'function', }, { inputs: [ { internalType: 'address', name: 'to', type: 'address', }, { internalType: 'uint256', name: 'amount', type: 'uint256', }, ], name: 'transfer', outputs: [ { internalType: 'bool', name: '', type: 'bool', }, ], stateMutability: 'nonpayable', type: 'function', }, { inputs: [ { internalType: 'address', name: 'from', type: 'address', }, { internalType: 'address', name: 'to', type: 'address', }, { internalType: 'uint256', name: 'amount', type: 'uint256', }, ], name: 'transferFrom', outputs: [ { internalType: 'bool', name: '', type: 'bool', }, ], stateMutability: 'nonpayable', type: 'function', }, ];TokenBridge Relayer ABI
TokenRelayer.jsexport default [ { inputs: [ { internalType: 'uint16', name: 'targetChainId', type: 'uint16', }, { internalType: 'address', name: 'token', type: 'address', }, { internalType: 'uint8', name: 'decimals', type: 'uint8', }, ], name: 'calculateRelayerFee', outputs: [ { internalType: 'uint256', name: 'feeInTokenDenomination', type: 'uint256', }, ], stateMutability: 'view', type: 'function', }, { inputs: [ { internalType: 'address', name: 'token', type: 'address', }, { internalType: 'uint256', name: 'amount', type: 'uint256', }, { internalType: 'uint256', name: 'toNativeTokenAmount', type: 'uint256', }, { internalType: 'uint16', name: 'targetChain', type: 'uint16', }, { internalType: 'bytes32', name: 'targetRecipient', type: 'bytes32', }, { internalType: 'uint32', name: 'batchId', type: 'uint32', }, ], name: 'transferTokensWithRelay', outputs: [ { internalType: 'uint64', name: 'messageSequence', type: 'uint64', }, ], stateMutability: 'payable', type: 'function', }, { inputs: [ { internalType: 'uint256', name: 'toNativeTokenAmount', type: 'uint256', }, { internalType: 'uint16', name: 'targetChain', type: 'uint16', }, { internalType: 'bytes32', name: 'targetRecipient', type: 'bytes32', }, { internalType: 'uint32', name: 'batchId', type: 'uint32', }, ], name: 'wrapAndTransferEthWithRelay', outputs: [ { internalType: 'uint64', name: 'messageSequence', type: 'uint64', }, ], stateMutability: 'payable', type: 'function', }, ];Batch Precompile ABI
Batch.jsexport default [ { anonymous: false, inputs: [ { indexed: false, internalType: 'uint256', name: 'index', type: 'uint256', }, ], name: 'SubcallFailed', type: 'event', }, { anonymous: false, inputs: [ { indexed: false, internalType: 'uint256', name: 'index', type: 'uint256', }, ], name: 'SubcallSucceeded', type: 'event', }, { inputs: [ { internalType: 'address[]', name: 'to', type: 'address[]', }, { internalType: 'uint256[]', name: 'value', type: 'uint256[]', }, { internalType: 'bytes[]', name: 'callData', type: 'bytes[]', }, { internalType: 'uint64[]', name: 'gasLimit', type: 'uint64[]', }, ], name: 'batchAll', outputs: [], stateMutability: 'nonpayable', type: 'function', }, { inputs: [ { internalType: 'address[]', name: 'to', type: 'address[]', }, { internalType: 'uint256[]', name: 'value', type: 'uint256[]', }, { internalType: 'bytes[]', name: 'callData', type: 'bytes[]', }, { internalType: 'uint64[]', name: 'gasLimit', type: 'uint64[]', }, ], name: 'batchSome', outputs: [], stateMutability: 'nonpayable', type: 'function', }, { inputs: [ { internalType: 'address[]', name: 'to', type: 'address[]', }, { internalType: 'uint256[]', name: 'value', type: 'uint256[]', }, { internalType: 'bytes[]', name: 'callData', type: 'bytes[]', }, { internalType: 'uint64[]', name: 'gasLimit', type: 'uint64[]', }, ], name: 'batchSomeUntilFailure', outputs: [], stateMutability: 'nonpayable', type: 'function', }, ];
Build the Transfer Multiassets Extrinsic¶
You can begin to tackle the xTokens.transferMultiassets extrinsic, which accepts four parameters:
assets- defines the multilocation and amount of xcDEV (xcGLMR for Moonbeam) and the local XC-20 to send to Moonbase Alpha, with the xcDEV positioned as the first asset and the local XC-20 as the secondfeeItem- set to the index of the xcDEV asset, which in this case is0, so that DEV is used to pay for the execution fees in Moonbase Alphadest- a multilocation that defines the Computed Origin account that you calculated in the previous section on Moonbase AlphadestWeightLimit- the weight to be purchased to pay for XCM execution on the destination chain
You can find more information on each parameter in the X-Tokens Precompile page documentation.
In the build-transfer-multiassets-call.js file, you'll build the xTokens.transferMultiassets extrinsic and export it.
import { ApiPromise, WsProvider } from '@polkadot/api';
// Input data
const originChainProviderWsURL = 'INSERT_ORIGIN_CHAIN_WSS_URL';
const computedOriginAccount = 'INSERT_COMPUTED_ORIGIN_ADDRESS';
const localXC20Address = 'INSERT_LOCAL_XC20_ADDRESS';
const transferAmount = 'INSERT_AMOUNT_TO_TRANSFER';
// Transfer multiassets parameters
const assets = {
V4: [
{
// xcDEV
id: {
parents: 1,
interior: {
X2: [
{ Parachain: 1000 }, // Parachain ID
{ PalletInstance: 3 }, // Index of the Balances Pallet
],
},
},
fun: {
Fungible: '100000000000000000', // 0.1 DEV as an estimation for XCM and EVM transaction fee
},
},
{
// Local XC-20 token
id: {
parents: 1,
interior: {
X3: [
{ Parachain: 1000 }, // Parachain ID
{ PalletInstance: 48 }, // Index of the ERC-20 XCM Bridge Pallet
{
AccountKey20: {
key: localXC20Address,
},
},
],
},
},
fun: {
Fungible: transferAmount,
},
},
],
};
const feeItem = 0;
const destination = {
V4: {
parents: 1,
interior: {
X2: [
{ Parachain: 1000 },
{ AccountKey20: { key: computedOriginAccount } },
],
},
},
};
const weightLimit = 'Unlimited';
export const getTransferMultiassetsCall = async () => {
// Create origin chain API provider
const originChainProvider = new WsProvider(originChainProviderWsURL);
const originChainAPI = await ApiPromise.create({
provider: originChainProvider,
});
// Create the transferMultiasset extrinsic
const transferMultiassets = originChainAPI.tx.xTokens.transferMultiassets(
assets,
feeItem,
destination,
weightLimit
);
originChainAPI.disconnect();
return transferMultiassets;
};
To modify the code for Moonbeam, you'll use the following configurations:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Parachain ID | 2004 |
| Balances Pallet Index | 10 |
| ERC-20 XCM Bridge Pallet Index | 110 |
Build the Remote EVM Call¶
To generate the second call of the batch transaction, the polkadotXcm.send extrinsic, you'll need to create the EVM transaction and then assemble the XCM instructions that execute said EVM transaction.
For now, you'll focus on generating the calldata for the EVM transaction. For this, you'll construct a transaction that interacts with the Batch Precompile so that two transactions can happen in one. This is helpful because this EVM transaction has to approve both a Wormhole relayer to relay the local XC-20 token and the relay action itself.
To create the batch transaction and wrap it in a remote EVM call to be executed on Moonbeam, you'll need to take the following steps:
-
Create contract instances of the local XC-20, the Wormhole relayer, and the Batch Precompile. For this, you'll need the ABI for each contract and the address of a Wormhole relayer. You can use the xLabs relayer:
0xcafd2f0a35a4459fa40c0517e17e6fa2939441ca0x9563a59c15842a6f322b10f69d1dd88b41f2e97b -
Use Ether's
encodeFunctionDatafunction to get the encoded call data for the two calls in the batch transaction: theapprovetransaction and thetransferTokensWithRelaytransaction - Combine the two transactions into a batch transaction and use Ether's
encodeFunctionDatato get the encoded call data for the batch transaction - Use the encoded call data for the batch transaction to create the remote EVM call via the
ethereumXcm.transactextrinsic, which accepts thexcmTransactionas the parameter. For more information, please refer to the Remote EVM Calls documentation
In the build-remote-calldata.js file, add the following code:
import { ApiPromise, WsProvider } from '@polkadot/api';
import { ethers } from 'ethers';
import batchABI from './abi/Batch.js';
import erc20ABI from './abi/ERC20.js';
import tokenRelayerABI from './abi/TokenRelayer.js';
const localXC20Address = 'INSERT_LOCAL_XC20_ADDRESS';
const transferAmount = 'INSERT_AMOUNT_TO_TRANSFER';
const xLabsRelayer = '0x9563a59c15842a6f322b10f69d1dd88b41f2e97b';
const destinationChainId = 'INSERT_DESTINATION_CHAIN_ID';
const computedOriginAccount = 'INSERT_COMPUTED_ORIGIN_ADDRESS';
// The recipient address on the destination chain needs to be formatted in 32 bytes
// You'll pad the address to the left with zeroes. Add the destination address below
// without the 0x
const destinationAddress =
'0x000000000000000000000000' + 'INSERT_DESTINATION_ADDRESS';
// Create contract instances
const batchInterface = new ethers.Interface(batchABI);
const localXC20Interface = new ethers.Interface(erc20ABI);
const tokenRelayer = new ethers.Contract(
xLabsRelayer,
tokenRelayerABI,
new ethers.JsonRpcProvider('https://rpc.api.moonbase.moonbeam.network')
);
// Get the encoded calldata for the approve transaction
const approve = localXC20Interface.encodeFunctionData('approve', [
xLabsRelayer, // Spender
transferAmount, // Amount
]);
// Get the encoded calldata for the transferTokensWithRelay transaction.
// Use wrapAndTransferEthWithRelay if the token is GLMR
const transferTokensWithRelay = tokenRelayer.interface.encodeFunctionData(
'transferTokensWithRelay',
[
localXC20Address, // Token
transferAmount, // Amount to be transferred
0, // Amount to swap into native assets on the target chain
destinationChainId, // Target chain ID, like Ethereum MainNet or Fantom
destinationAddress, // Target recipient address
0, // Batch ID for Wormhole message batching
]
);
const encodedBatchAllCall = batchInterface.encodeFunctionData('batchAll', [
[localXC20Address, xLabsRelayer], // Addresses to call
[0, 0], // Value to send for each call
[approve, transferTokensWithRelay], // Call data for each call
[], // Gas limit for each call
]);
export const getTransactCall = async () => {
// Create Moonbeam API provider
const moonbeamProvider = new WsProvider(
'wss://wss.api.moonbase.moonbeam.network'
);
const moonbeamAPI = await ApiPromise.create({ provider: moonbeamProvider });
// Create the extrinsic for the remote EVM call
const transact = moonbeamAPI.tx.ethereumXcm.transact({
V2: {
gasLimit: 350000n,
action: {
Call: '0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000808',
},
value: 0n,
input: encodedBatchAllCall,
},
});
const txWeight = (await transact.paymentInfo(computedOriginAccount)).weight;
moonbeamAPI.disconnect();
return { transact, txWeight };
};
Build the XCM Message for the Remote EVM Call¶
Next, you'll need to create the extrinsic to send the remote EVM call to Moonbeam. To do so, you'll want to send an XCM message such that the Transact XCM instruction gets successfully executed. The most common method to do this is through polkadotXcm.send with the WithdrawAsset, BuyExecution, and Transact instructions. RefundSurplus and DepositAsset can also be used to ensure no assets get trapped, but they are technically optional.
In the build-remote-evm-call.js file, add the following code:
import { ApiPromise, WsProvider } from '@polkadot/api';
import { getTransactCall } from './build-batch-evm-call.js';
const originChainProviderWsURL = 'INSERT_ORIGIN_CHAIN_WSS_URL';
const computedOriginAccount = 'INSERT_COMPUTED_ORIGIN_ADDRESS';
export const getPolkadotXcmCall = async () => {
// Create origin chain API provider
const originChainProvider = new WsProvider(originChainProviderWsURL);
const originChainAPI = await ApiPromise.create({
provider: originChainProvider,
});
// Get the weight required to execute the Transact calldata
const { transact, txWeight } = await getTransactCall();
// Create the extrinsic for the remote EVM call
const sendXcm = originChainAPI.tx.polkadotXcm.send(
{ V4: { parents: 1, interior: { X1: [{ Parachain: 1000 }] } } },
{
V4: [
{
// Withdraw DEV asset (0.06) from the target account
WithdrawAsset: [
{
id: {
parents: 0,
interior: { X1: [{ PalletInstance: 3 }] },
},
fun: { Fungible: 60000000000000000n },
},
],
},
{
// Buy execution with the DEV asset
BuyExecution: {
fees: {
id: {
parents: 0,
interior: { X1: [{ PalletInstance: 3 }] },
},
fun: { Fungible: 60000000000000000n },
},
weightLimit: 'Unlimited',
},
},
{
Transact: {
originKind: 'SovereignAccount',
requireWeightAtMost: {
refTime: txWeight.refTime,
proofSize: txWeight.proofSize,
},
call: {
encoded: transact.method.toHex(),
},
},
},
{
RefundSurplus: {},
},
{
DepositAsset: {
// Note that this must be AllCounted and not All, since All has too high of a gas requirement
assets: { Wild: { AllCounted: 1 } },
beneficiary: {
parents: 0,
interior: {
X1: [{ AccountKey20: { key: computedOriginAccount } }],
},
},
},
},
],
}
);
return sendXcm;
};
Build the Batch Extrinsic¶
To ensure that both the xTokens.transferMultiassets and the polkadotXcm.send transactions are sent together, you can batch them together using utility.batchAll. This helps ensure that the asset transfer happens before the EVM transaction, which is a necessary distinction. Unfortunately, this is subject to change with future XCM updates.
In the send-batch-transaction.js file, add the following code:
import { ApiPromise, WsProvider, Keyring } from '@polkadot/api';
import { cryptoWaitReady } from '@polkadot/util-crypto';
import { getTransferMultiassetsCall } from './build-transfer-multiassets-call.js';
import { getPolkadotXcmCall } from './build-remote-evm-call.js';
const originChainProviderWsURL = 'INSERT_ORIGIN_CHAIN_WSS_URL';
const sendBatchTransaction = async () => {
// Create origin chain API provider
const originChainProvider = new WsProvider(originChainProviderWsURL);
const originChainAPI = await ApiPromise.create({
provider: originChainProvider,
});
// Create the batch transaction
const batchTransaction = originChainAPI.tx.utility.batchAll([
await getTransferMultiassetsCall(),
await getPolkadotXcmCall(),
]);
// Create a keyring instance to sign the transaction
await cryptoWaitReady();
const keyring = new Keyring({ type: 'ethereum' });
const account = keyring.addFromUri(privateKey);
// Send the batch transaction
const transaction = await batchTransaction.signAndSend(account, ({ status }) => {
if (status.isInBlock) console.log(`Transaction sent!`);
});
originChainAPI.disconnect();
return transaction;
};
sendBatchTransaction();
If you want to see an example project that fully implements this, an example is available in a GitHub repository.
It's important to note that not every parachain will have X-Tokens and the other pallets implemented in a way that will allow this path. Substrate-based chains are very flexible, to the point where a standard doesn't exist. If you believe your parachain does not support this path, please provide an alternative solution in the Moonbeam forum and to the Wormhole team.
Tokens Available Through Wormhole¶
While Wormhole has the technical capability to bridge any token across chains, relayers will not support every token for fees. The ERC-20 assets that can be bridged through Wormhole's MRL solution depend on the tokens the xLabs relayer takes in. The tokens that are available to Moonbeam and Moonbase Alpha are listed in the table below:
| Token Name | Symbol | Decimals | Address |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wrapped AVAX | wAVAX | 18 | 0xd4937A95BeC789CC1AE1640714C61c160279B22F |
| Wrapped Bitcoin | wBTC | 8 | 0xE57eBd2d67B462E9926e04a8e33f01cD0D64346D |
| Wrapped BNB | wBNB | 18 | 0xE3b841C3f96e647E6dc01b468d6D0AD3562a9eeb |
| Celo Native Asset | CELO | 18 | 0xc1a792041985F65c17Eb65E66E254DC879CF380b |
| Dai Stablecoin | DAI | 18 | 0x06e605775296e851FF43b4dAa541Bb0984E9D6fD |
| Wrapped Ethereum | wETH | 18 | 0xab3f0245B83feB11d15AAffeFD7AD465a59817eD |
| Wrapped Fantom | wFTM | 18 | 0x609AedD990bf45926bca9E4eE988b4Fb98587D3A |
| Wrapped GLMR | wGLMR | 18 | 0xAcc15dC74880C9944775448304B263D191c6077F |
| Wrapped Matic | wMATIC | 18 | 0x82DbDa803bb52434B1f4F41A6F0Acb1242A7dFa3 |
| Wrapped SOL | SOL | 9 | 0x99Fec54a5Ad36D50A4Bba3a41CAB983a5BB86A7d |
| Sui | SUI | 9 | 0x484eCCE6775143D3335Ed2C7bCB22151C53B9F49 |
| Tether USD | USDT | 6 | 0xc30E9cA94CF52f3Bf5692aaCF81353a27052c46f |
| USDC (Wormhole) | USDC | 6 | 0x931715FEE2d06333043d11F658C8CE934aC61D0c |
| Token Name | Symbol | Decimals | Address |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wrapped Avax | wAVAX | 18 | 0x2E8afeCC19842229358f3650cc3F091908dcbaB4 |
| Wrapped BNB | wBNB | 18 | 0x6097E80331B0c6aF4F74D7F2363E70Cb2Fd078A5 |
| Celo Native Asset | CELO | 18 | 0x3406a9b09adf0cb36DC04c1523C4b294C6b79513 |
| Dai Stablecoin | DAI | 18 | 0xc31EC0108D8e886be58808B4C2C53f8365f1885D |
| Wrapped Ether | wETH | 18 | 0xD909178CC99d318e4D46e7E66a972955859670E1 |
| Wrapped Ether (Wormhole) | wETH | 18 | 0xd27d8883E31FAA11B2613b14BE83ad8951C8783C |
| Wrapped Fantom | wFTM | 18 | 0x566c1cebc6A4AFa1C122E039C4BEBe77043148Ee |
| Wrapped Matic | wMATIC | 18 | 0xD2888f015BcB76CE3d27b6024cdEFA16836d0dbb |
| Sui | SUI | 9 | 0x2ed4B5B1071A3C676664E9085C0e3826542C1b27 |
| USDC | USDC | 6 | 0x6533CE14804D113b1F494dC56c5D60A43cb5C3b5 |
Please take the time to verify that these assets are still Wormhole assets on Moonbeam by using the Wormhole asset verifier.
| Created: June 22, 2023