Use API3 To Request Off-Chain Data on Moonbeam¶
Introduction¶
API3 is a decentralized solution for delivering traditional API services to smart contract platforms in an easily accessible and scalable way. It is governed by a Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO), the API3 DAO. API3 enables developers to access off-chain resources from within their smart contracts without worrying about security implications. API3 makes this possible through Airnodes, which are first-party oracles, and on-chain data feeds sourced from these oracles.
Developers can use Airnode to request off-chain data inside their smart contracts on Moonbeam networks. An Airnode is a first-party oracle that pushes off-chain API data to your on-chain contract. Airnode lets API providers easily run their own first-party oracle nodes. That way, they can provide data to any on-chain dApp interested in their services, all without an intermediary.
An on-chain smart contract requests the RRP (Request Response Protocol) contract (AirnodeRrpV0.sol) that adds the request to the event logs. The Airnode then accesses the event logs, fetches the API data, and performs a callback to the requester with the requested data.
Request Off-Chain Data From an Airnode¶
Requesting off-chain data essentially involves triggering an Airnode and getting its response through your smart contract. The smart contract in this case would be the requester contract, which will make a request to the desired off-chain Airnode and then capture its response.
The requester calling an Airnode primarily focuses on two tasks:
- Making the request
- Accepting and decoding the response
Here is an example of a basic requester contract to request data from an Airnode:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity 0.8.9;
import "@api3/airnode-protocol/contracts/rrp/requesters/RrpRequesterV0.sol";
import "@openzeppelin/contracts@4.9.5/access/Ownable.sol";
// A Requester that will return the requested data by calling the specified Airnode.
contract Requester is RrpRequesterV0, Ownable {
mapping(bytes32 => bool) public incomingFulfillments;
mapping(bytes32 => int256) public fulfilledData;
// Make sure you specify the right _rrpAddress for your chain while deploying the contract.
constructor(address _rrpAddress) RrpRequesterV0(_rrpAddress) {}
// To receive funds from the sponsor wallet and send them to the owner.
receive() external payable {
payable(owner()).transfer(address(this).balance);
}
// The main makeRequest function that will trigger the Airnode request.
function makeRequest(
address airnode,
bytes32 endpointId,
address sponsor,
address sponsorWallet,
bytes calldata parameters
) external {
bytes32 requestId = airnodeRrp.makeFullRequest(
airnode, // airnode address
endpointId, // endpointId
sponsor, // sponsor's address
sponsorWallet, // sponsorWallet
address(this), // fulfillAddress
this.fulfill.selector, // fulfillFunctionId
parameters // encoded API parameters
);
incomingFulfillments[requestId] = true;
}
function fulfill(bytes32 requestId, bytes calldata data)
external
onlyAirnodeRrp
{
require(incomingFulfillments[requestId], "No such request made");
delete incomingFulfillments[requestId];
int256 decodedData = abi.decode(data, (int256));
fulfilledData[requestId] = decodedData;
}
// To withdraw funds from the sponsor wallet to the contract.
function withdraw(address airnode, address sponsorWallet) external onlyOwner {
airnodeRrp.requestWithdrawal(
airnode,
sponsorWallet
);
}
}
You can also try deploying the example contract on Remix.
Contract Addresses¶
The _rrpAddress is the main airnodeRrpAddress. The RRP contracts have already been deployed on-chain. The addresses for the _rrpAddress on Moonbeam networks are as follows:
| Contract | Addresses |
|---|---|
| AirnodeRrpV0 | 0xa0AD79D995DdeeB18a14eAef56A549A04e3Aa1Bd |
| Contract | Addresses |
|---|---|
| AirnodeRrpV0 | 0xa0AD79D995DdeeB18a14eAef56A549A04e3Aa1Bd |
| Contract | Addresses |
|---|---|
| AirnodeRrpV0 | 0xa0AD79D995DdeeB18a14eAef56A549A04e3Aa1Bd |
Request Parameters¶
The makeRequest() function expects the following parameters to make a valid request:
airnode- specifies the Airnode addressendpointId- specifies which endpoint to be usedsponsorandsponsorWallet- specifies which wallet will be used to fulfill the requestparameters- specifies the API and Reserved Parameters (see Airnode ABI specifications for how these are encoded). Parameters can be encoded off-chain using the@airnode-abilibrary
Response Parameters¶
The callback to the requester contract contains two parameters:
requestId- first acquired when making the request and passed here as a reference to identify the request for which the response is intendeddata- in case of a successful response, this is the requested data encoded and contains a timestamp in addition to other response data. Decode it using thedecode()function from theabiobject
Note
Sponsors should not fund a sponsorWallet with more than they can trust the Airnode with, as the Airnode controls the private key to the sponsorWallet. The deployer of such Airnode undertakes no custody obligations, and the risk of loss or misuse of any excess funds sent to the sponsorWallet remains with the sponsor.
dAPIs: API3 Data Feeds¶
dAPIs are continuously updated streams of off-chain data, such as the latest cryptocurrency, stock, and commodity prices. They can power decentralized applications such as DeFi lending, synthetic assets, stablecoins, derivatives, NFTs, and more.
The data feeds are continuously updated by first-party oracles using signed data. DApp owners can read the on-chain value of any dAPI in real-time.
Because they are composed of first-party data feeds, dAPIs offer security, transparency, cost-efficiency, and scalability in a turnkey package.
To learn more about how dAPIs work, please refer to API3's documentation.
Subscribe to dAPIs¶
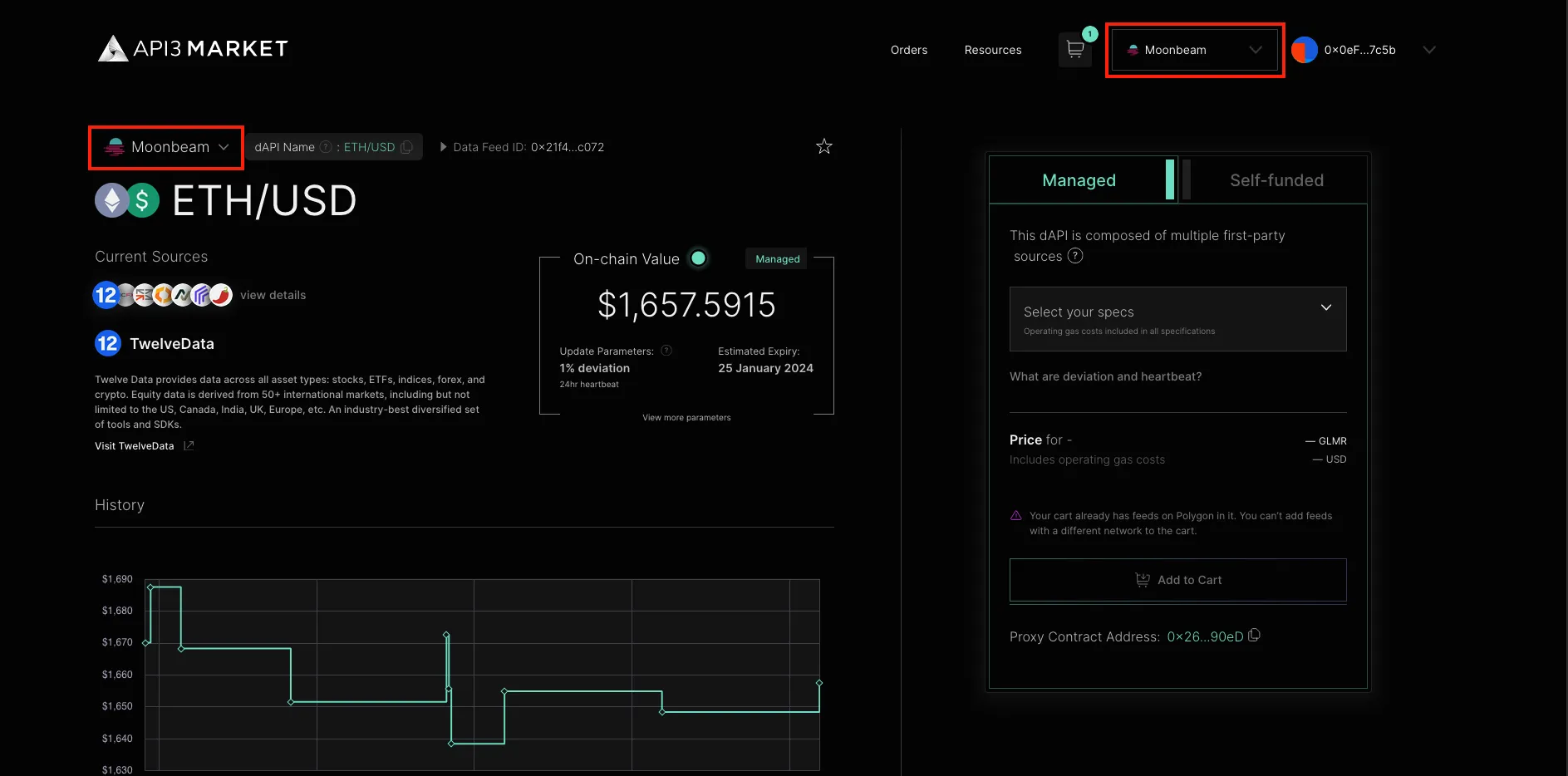
The API3 Market lets users access dAPIs on Moonbeam, Moonriver, and the Moonbase Alpha TestNet (currently labeled as the Moonbeam TestNet).
From the API3 Market home page, you can search for a given chain. After selecting the chain, you can view the list of available dAPIs and click on one for more information. For example, you can click on the USDT/USD pair available for Moonbeam to view the parameters of the dAPI, including the deviation and the heartbeat.
The supported parameters for dAPIs are:
| Deviation | Heartbeat |
|---|---|
| 0.25% | 24 hours |
| 0.5% | 24 hours |
| 1% | 24 hours |
| 5% | 24 hours |
Configure and Activate a dAPI¶
Once you've selected a dAPI to interact with, check the expiration date and update the parameters as needed. You can update the parameters and extend the subscription by purchasing a new configuration. If the dAPI has been activated and the configurations listed will work for you, you can skip ahead to the next section to learn how to interact with the dAPI.
To purchase a plan with new configurations, click on Purchase new plan and take the following steps:
- Select your parameters
- Click on Connect Wallet
Once connected, you'll be able to purchase your new plan. Click on Purchase and sign the transaction. After the transaction has been confirmed, you will be able to see the updated configuration for the dAPI.
Get Data from a dAPI¶
To interact with a dAPI, you'll need to get the proxy address for it. Click on the Integrate button from the dAPI details page. Then, on the integration page, copy the proxy address.
With the proxy address in hand, you'll be able to integrate the dAPI into a smart contract. Here's an example of a basic contract that reads from a dAPI:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity 0.8.17;
import "@openzeppelin/contracts@4.9.5/access/Ownable.sol";
import "@api3/contracts/api3-server-v1/proxies/interfaces/IProxy.sol";
contract DataFeedReaderExample is Ownable {
// The proxy contract address obtained from the API3 Market UI
address public proxyAddress;
// Updating the proxy contract address is a security-critical
// action. In this example, only the owner is allowed to do so
function setProxyAddress(address _proxyAddress) public onlyOwner {
proxyAddress = _proxyAddress;
}
function readDataFeed()
external
view
returns (int224 value, uint256 timestamp)
{
// Use the IProxy interface to read a dAPI via its
// proxy contract
(value, timestamp) = IProxy(proxyAddress).read();
// If you have any assumptions about `value` and `timestamp`,
// make sure to validate them after reading from the proxy
}
}
The example contract contains two functions:
setProxyAddress()- used to set the address of the dAPI proxy contractreadDataFeed()- aviewfunction that returns the latest price of the set dAPI
Additional Resources¶
Here are some additional developer resources:
| Created: January 3, 2023