How to Use Chopsticks to Fork Moonbeam¶
Introduction¶
Chopsticks provides a developer-friendly method of locally forking existing Substrate based chains. It allows for the replaying of blocks to easily examine how extrinsics effect state, the forking of multiple blocks for XCM testing, and more. This allows developers to test and experiment with their own custom blockchain configurations in a local development environment, without the need to deploy a live network.
Overall, Chopsticks aims to simplify the process of building blockchain applications on Substrate and make it accessible to a wider range of developers.
Forking Moonbeam with Chopsticks¶
To use Chopsticks, you can install it as a package with the Node package manager or Yarn:
npm i @acala-network/chopsticks@latest
Once installed, you can run commands with the Node package executor. For example, this runs Chopstick's base command:
npx @acala-network/chopsticks@latest
To run Chopsticks, you will need some sort of configuration, typically through a file. Chopsticks' source repository includes a set of YAML configuration files that can be used to create a local copy of a variety of Substrate chains. You can download the configuration files from the source repository's configs folder.
Moonbeam, Moonriver, and Moonbase Alpha all have default files available:
endpoint: wss://wss.api.moonbeam.network
mock-signature-host: true
db: ./db.sqlite
import-storage:
System:
Account:
-
-
- "0xf24FF3a9CF04c71Dbc94D0b566f7A27B94566cac"
- data:
free: "100000000000000000000000"
TechCommitteeCollective:
Members: ["0xf24FF3a9CF04c71Dbc94D0b566f7A27B94566cac"]
CouncilCollective:
Members: ["0xf24FF3a9CF04c71Dbc94D0b566f7A27B94566cac"]
TreasuryCouncilCollective:
Members: ["0xf24FF3a9CF04c71Dbc94D0b566f7A27B94566cac"]
AuthorFilter:
EligibleRatio: 100
EligibleCount: 100
endpoint: wss://wss.moonriver.moonbeam.network
mock-signature-host: true
db: ./db.sqlite
import-storage:
System:
Account:
-
-
- "0xf24FF3a9CF04c71Dbc94D0b566f7A27B94566cac"
- data:
free: "100000000000000000000000"
TechCommitteeCollective:
Members: ["0xf24FF3a9CF04c71Dbc94D0b566f7A27B94566cac"]
CouncilCollective:
Members: ["0xf24FF3a9CF04c71Dbc94D0b566f7A27B94566cac"]
TreasuryCouncilCollective:
Members: ["0xf24FF3a9CF04c71Dbc94D0b566f7A27B94566cac"]
AuthorFilter:
EligibleRatio: 100
EligibleCount: 100
endpoint: wss://wss.api.moonbase.moonbeam.network
mock-signature-host: true
db: ./db.sqlite
import-storage:
System:
Account:
-
-
- "0xf24FF3a9CF04c71Dbc94D0b566f7A27B94566cac"
- data:
free: "100000000000000000000000"
TechCommitteeCollective:
Members: ["0xf24FF3a9CF04c71Dbc94D0b566f7A27B94566cac"]
CouncilCollective:
Members: ["0xf24FF3a9CF04c71Dbc94D0b566f7A27B94566cac"]
TreasuryCouncilCollective:
Members: ["0xf24FF3a9CF04c71Dbc94D0b566f7A27B94566cac"]
Sudo:
Key: "0xf24FF3a9CF04c71Dbc94D0b566f7A27B94566cac"
AuthorFilter:
EligibleRatio: 100
EligibleCount: 100
These are the settings that can be included in the config file:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
genesis | The link to a parachain's raw genesis file to build the fork from, instead of an endpoint. |
timestamp | Timestamp of the block to fork from. |
endpoint | The endpoint of the parachain to fork. |
block | Use to specify at which block hash or number to replay the fork. |
wasm-override | Path of the WASM to use as the parachain runtime, instead of an endpoint's runtime. |
db | Path to the name of the file that stores or will store the parachain's database. |
config | Path or URL of the config file. |
port | The port to expose an endpoint on. |
build-block-mode | How blocks should be built in the fork: batch, manual, instant. |
import-storage | A pre-defined JSON/YAML storage file path to override in the parachain's storage. |
allow-unresolved-imports | Whether to allow WASM unresolved imports when using a WASM to build the parachain. |
html | Include to generate storage diff preview between blocks. |
mock-signature-host | Mock signature host so that any signature starts with 0xdeadbeef and filled by 0xcd is considered valid. |
You can use the configuration file with the base command npx @acala-network/chopsticks@latest to fork assets by providing it with the --config flag.
You can use a raw GitHub URL of the default configuration files, a path to a local configuration file, or simply use the chain's name for the --config flag. For example, the following commands all use Moonbeam's configuration in the same way:
npx @acala-network/chopsticks@latest --config=moonbeam
npx @acala-network/chopsticks@latest \
--config=https://raw.githubusercontent.com/AcalaNetwork/chopsticks/master/configs/moonbeam.yml
npx @acala-network/chopsticks@latest --config=configs/moonbeam.yml
Note
If using a file path, make sure you've downloaded the Moonbeam configuration file, or have created your own.
A configuration file is not necessary, however. All of the settings (except genesis and timestamp) can also be passed as flags to configure the environment completely in the command line. For example, the following command forks Moonbase Alpha at block 100.
npx @acala-network/chopsticks@latest --endpoint wss://wss.api.moonbase.moonbeam.network --block 100
Quickstart¶
The simplest way to fork Moonbeam is through the configuration files that are stored in the Chopsticks GitHub repository:
npx @acala-network/chopsticks@latest \
--config=https://raw.githubusercontent.com/AcalaNetwork/chopsticks/master/configs/moonbeam.yml
npx @acala-network/chopsticks@latest \
--config=https://raw.githubusercontent.com/AcalaNetwork/chopsticks/master/configs/moonriver.yml
npx @acala-network/chopsticks@latest \
--config=https://raw.githubusercontent.com/AcalaNetwork/chopsticks/master/configs/moonbase-alpha.yml
Interacting with a Fork¶
When running a fork, by default it will be accessible at:
ws://localhost:8000
You will be able to interact with the parachain via libraries such as Polkadot.js and its user interface, Polkadot.js Apps.
You can interact with Chopsticks via the Polkadot.js Apps hosted user interface. To do so, visit the page and take the following steps:
- Click the icon in the top left
- Go to the bottom and open Development
- Select the Custom endpoint and enter
ws://localhost:8000 - Click the Switch button
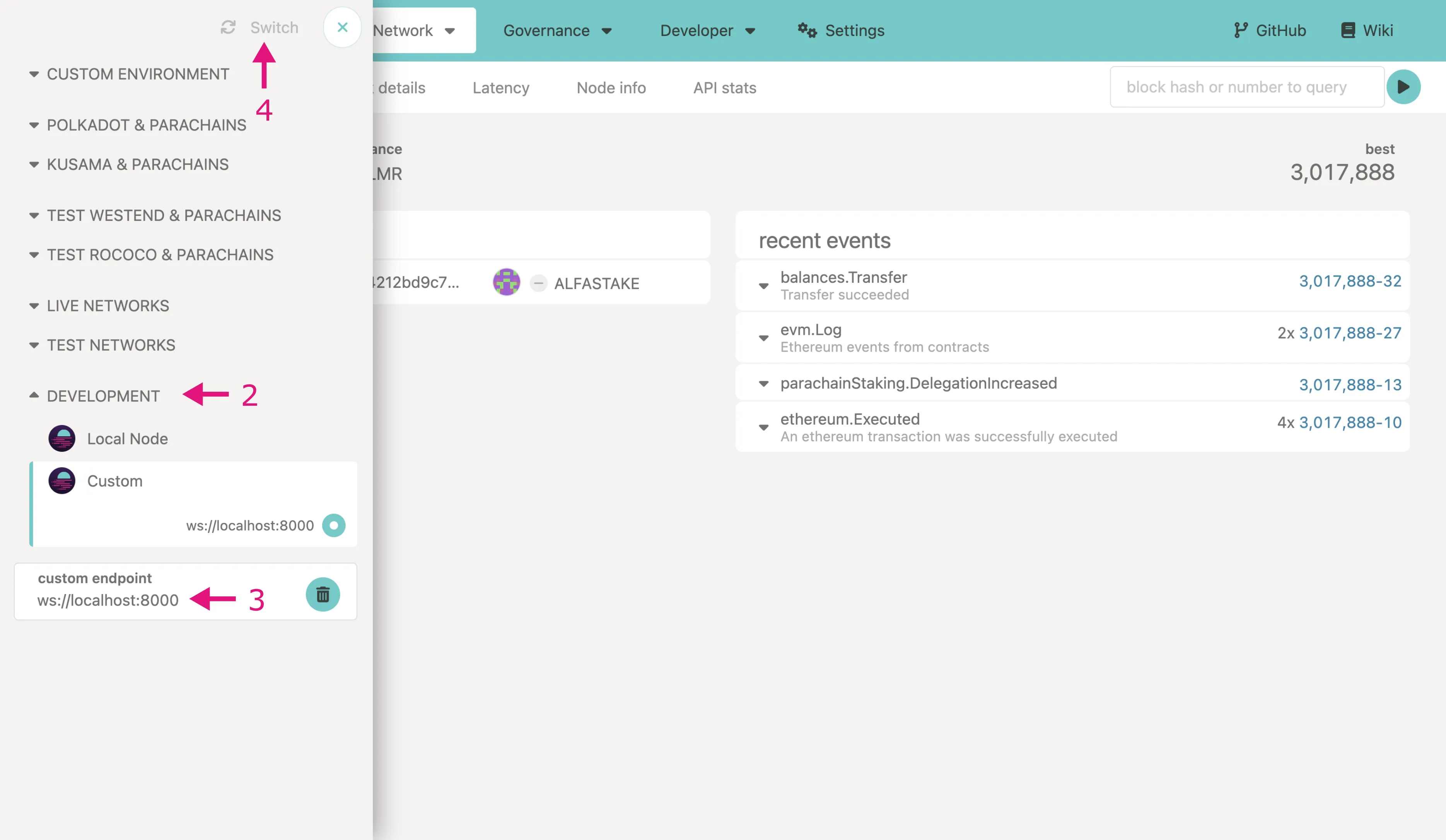
You should now be able to interact with the fork as you would an active parachain or relay chain.
Note
If your browser cannot connect to the WebSocket endpoint provided by Chopsticks, you might need to allow insecure connections for the Polkadot.js Apps URL. Another solution is to run the Docker version of Polkadot.js Apps.
Replaying Blocks¶
In the case where you would like to replay a block and retrieve its information to dissect the effects of an extrinsic, you can use the npx @acala-network/chopsticks@latest run-block command. Its following flags are:
| Flag | Description |
|---|---|
endpoint | The endpoint of the parachain to fork. |
block | Use to specify at which block hash or number to replay the fork. |
wasm-override | Path of the WASM to use as the parachain runtime, instead of an endpoint's runtime. |
db | Path to the name of the file that stores or will store the parachain's database. |
config | Path or URL of the config file. |
output-path=/[file_path] | Use to print out results to a JSON file instead of printing it out in the console. |
html | Include to generate an HTML representation of the storage diff preview between blocks. |
open | Whether to open the HTML representation. |
For example, running the following command will re-run Moonbeam's block 1000, and write the storage diff and other data in a moonbeam-output.json file:
npx @acala-network/chopsticks@latest run-block \
--endpoint wss://wss.api.moonbeam.network \
--output-path=./moonbeam-output.json \
--block 1000
XCM Testing¶
To test out XCM messages between networks, you can fork multiple parachains and a relay chain locally. For example, the following will fork Moonriver, Karura, and Kusama given that you've downloaded the configs directory from the source GitHub repository:
npx @acala-network/chopsticks@latest xcm \
--r=kusama.yml \
--p=moonriver.yml \
--p=karura.yml
You should see something like the following output:
[13:50:57.807] INFO (rpc/64805): Loading config file https://raw.githubusercontent.com/AcalaNetwork/chopsticks/master/configs/moonriver.yml
[13:50:59.655] INFO (rpc/64805): Moonriver RPC listening on port 8000
[13:50:59.656] INFO (rpc/64805): Loading config file https://raw.githubusercontent.com/AcalaNetwork/chopsticks/master/configs/karura.yml
[13:51:03.275] INFO (rpc/64805): Karura RPC listening on port 8001
[13:51:03.586] INFO (xcm/64805): Connected parachains [2000,2023]
[13:51:03.586] INFO (rpc/64805): Loading config file https://raw.githubusercontent.com/AcalaNetwork/chopsticks/master/configs/kusama.yml
[13:51:07.241] INFO (rpc/64805): Kusama RPC listening on port 8002
[13:51:07.700] INFO (xcm/64805): Connected relaychain 'Kusama' with parachain 'Moonriver'
[13:51:08.386] INFO (xcm/64805): Connected relaychain 'Kusama' with parachain 'Karura'
Including the r flag as the relay chain is optional, as Chopsticks will automatically mock a relay chain between networks. You can also use a raw GitHub URL or the name of a popular branch, similar to the base command.
WebSocket Commands¶
Chopsticks' internal websocket server has special endpoints that allows the manipulation of the local Substrate chain. These are the methods that can be invoked:
| Method | Parameters | Description |
|---|---|---|
dev_newBlock | options | Generates one or more new blocks. |
dev_setStorage | values, blockHash | Create or overwrite the value of any storage. |
dev_timeTravel | date | Sets the timestamp of the block to the date value. |
dev_setHead | hashOrNumber | Sets the head of the blockchain to a specific hash or number. |
The parameters above are formatted in the following ways:
| Parameter | Format | Example |
|---|---|---|
options | { "to": number, "count": number } | { "count": 5 } |
values | Object | { "Sudo": { "Key": "0x6Be02d1d3665660d22FF9624b7BE0551ee1Ac91b" } } |
blockHash | string | "0x1a34506b33e918a0106b100db027425a83681e2332fe311ee99d6156d2a91697" |
date | Date | "2030-08-15T00:00:00" |
hashOrNumber | number | string |
options{ "to": number, "count": number } - a JSON object where"to"will create blocks up to a certain value, and"count"will increase by a certain number of blocks. Use only one entry at a time within the JSON objectvaluesObject - a JSON object resembling the path to a storage value, similar to what you would retrieve via Polkadot.jsblockHashstring - optional, the blockhash at which the storage value is changeddateDate - a Date string (compatible with the JavaScript Date library) that will change the time stamp from which the next blocks being created will be at. All future blocks will be sequentially after that point in timehashOrNumbernumber | string - if found, the chain head will be set to the block with the block number or block hash of this value
Each method can be invoked by connecting to the websocket (ws://localhost:8000 by default) and sending the data and parameters in the following format. Replace METHOD_NAME with the name of the method, and replace or delete PARAMETER_1 and PARAMETER_2 with the parameter data relevant to the method:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"method": "METHOD_NAME",
"params": ["PARAMETER_1", "PARAMETER_2", "..."]
}
| Created: February 24, 2023